On this page
article
Assignment and Compound Assignment Operators
Assignment and Compound Assignment Operators
- Assignment Operator
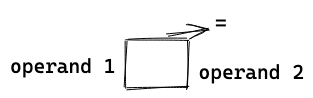
The assignment operator is used to save a value in the variable.
Type
Rust has only one assignment operator, = . The following table defines the function of the operator.
| operator | operation | explanation | example |
|---|---|---|---|
| operand1 = operand2 | assign a value | assign a value of operand 2 to operand 1 | a = 1 b = a |
The following example demonstrates the use of some of the assignment operator in a program:
fn main() {
let a = 2;
let b = a;
println!("b = a");
println!("Value of a:{}", a);
println!("Value of b:{}", b);
}
output:-
b = a
Value of a:2
Value of b:2
Compound Assignment Operator
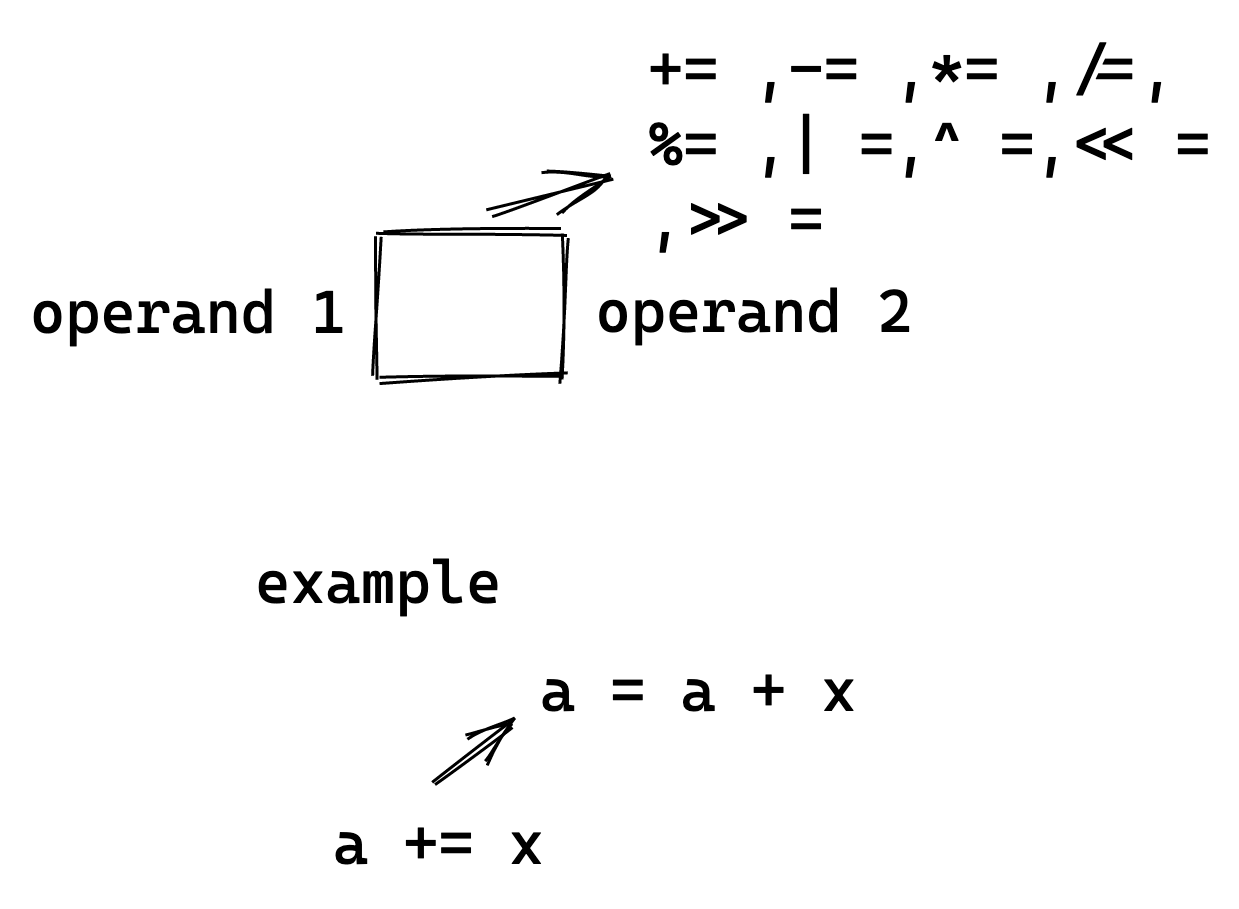
The compound assignment operator is used to perform an operation and then assign that value to the operand.
Types
The following table summarizes the types of compound assignment operators
| operator | operation | explanation |
|---|---|---|
| operand1 += operand2 operand1 -= operand2 | add a value and assign subtract a value and assign | add left-hand side to right-hand side and then save updated value to left operand add right-hand side to right-hand side and then save updated value to left operand |
| operand1 /= operand2 operand1 *= operand2 | divide a value and assign multiple a value and assign | divide left-hand side to right-hand side and then save updated value to left operand multiply left-hand side to right-hand side and then save updated value to left operand |
| operand1 %= operand2 | modulus and assign | take modulus of the left-hand side with right-hand operand and then save updated value to left operand |
| operand1 &= operand2 | Bitwise AND and assign | Bitwise AND of the left-hand side with right-hand operand and then save updated value to left operand |
| operand1 |= operand2 | Bitwise OR and assign | Bitwise OR of the left-hand side with right-hand operand and then save updated value to left operand |
| operand1 ^= operand2 | Bitwise XOR and assign | Bitwise XOR of the left-hand side with right-hand operand and then save updated value to left operand |
| «= operand1 | left sift and assign | left shift the operand x times then save updated value to operand |
| »= operand1 | right shift and assign | right shift the operand x times then save updated value to operand |
The following example demonstrates the use of some of these operators in a program:
Quiz
primaryColor: steelblue secondaryColor: ‘#e8e8e8’ textColor: black shuffleQuestions: false shuffleAnswers: true locale: en
Test your understanding of the assignment and compound assignment operators in Rust.
# What is the output of the following code?
```
fn main() {
let mut a = 2;
let mut b = 3;
a += a;
b -= b;
a *= 1;
b *= 3;
a -= 1;
println!("a: {}", a);
println!("b: {}", b);
}
```
- [ ] ```
a: 3
b: 0
```
- [ ] ```
a: 0
b: 3
```
- [ ] ```
a: 2
b: 0
```
- [ ] ```
a: 4
b: 3
```
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .