On this page
article
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise Operators
- What Are Bitwise Operators? Bitwise operators deal with the binary representation of the operands.
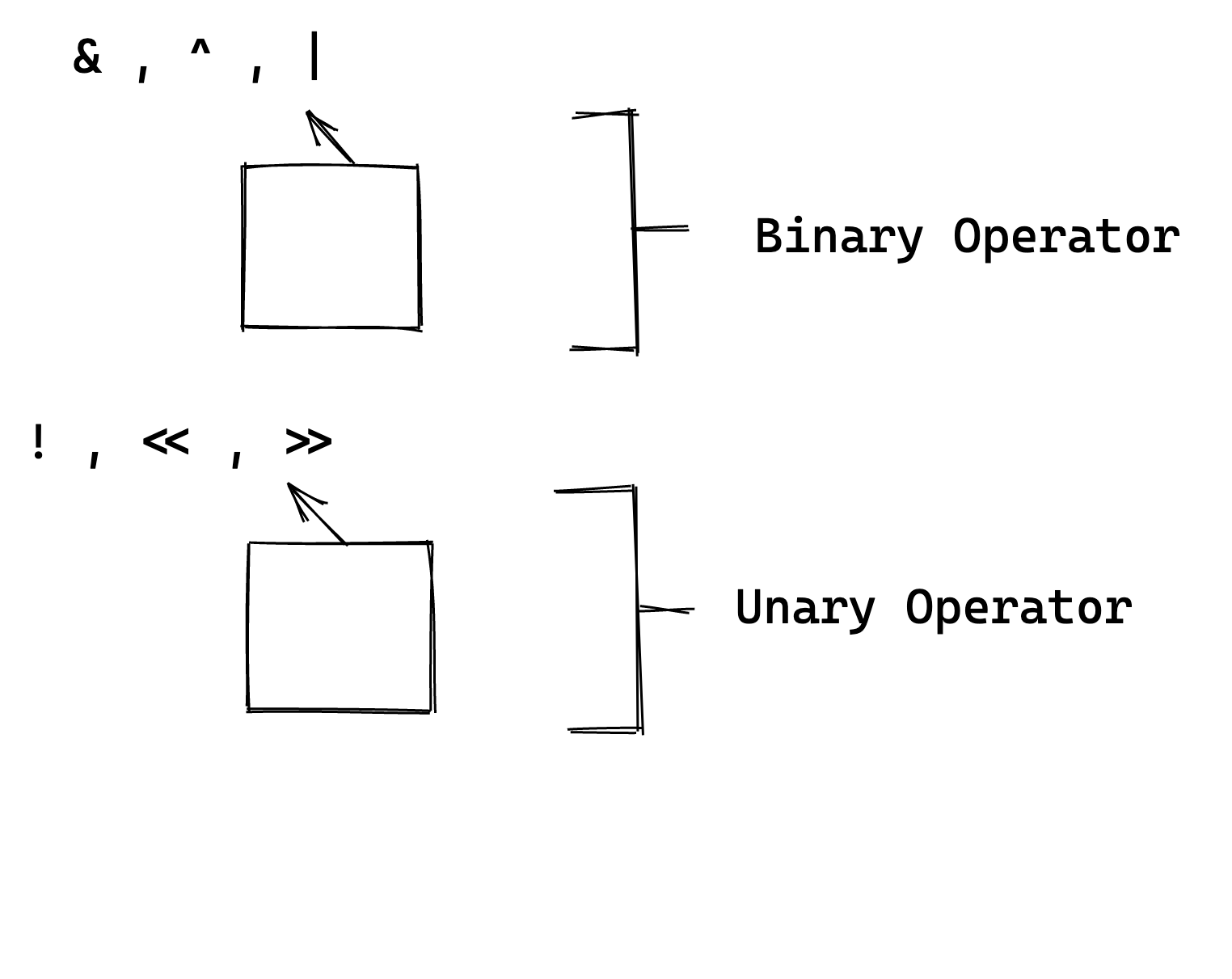
Types
The table below summarizes the types of bitwise operators in Rust.
| operator | operation | explanation |
|---|---|---|
| operand1 & operand2 | AND | bitwise AND operand1 and operand2 |
| operand1 | operand2 | OR | bitwise OR operand1 and operand2 |
| operand1 ^ operand2 | XOR | bitwise XOR operand1 and operand2 |
| ! operand1 | NOT | Inverse the bit of operand |
| « operand | Left shift | moves all the operand1 to the left by the number of places specified in the operand 2 new bits filled with zeros . shifting a value left by one position is equivalent to multiplying it by 2 , Shifting to positions is equivalent to multiplying it by 4 and so on |
| » operand | Right Shift | moves all the operand1 to the right by the number of places specified in the operand 2 new bits filled with zeros . shifting a value right by one position is equivalent to multiplying it by 2 , Shifting to positions is equivalent to multiplying it by 4 and so on |
📝 Note: Right shift » is same as arithmetic right shift on signed integer types, logical right shift on unsigned integer types.
Example
The example below shows the bitwise AND, OR, XOR, Left Shift, and Right Shift operations.
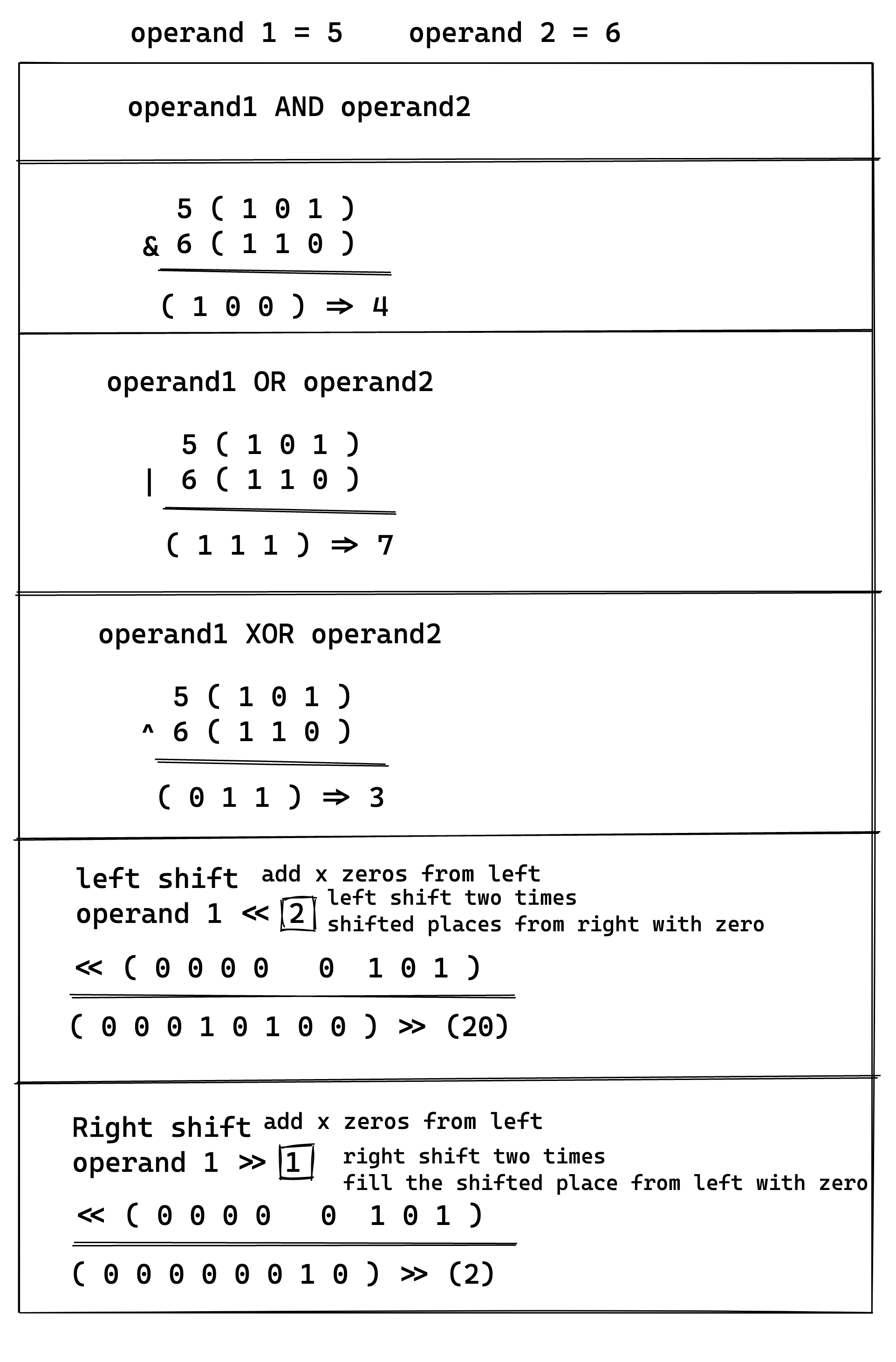
The following example shows the use of bitwise operators in a program:
fn main() {
let a = 5;
let b = 6;
println!("Operand 1: {}, Operand 2: {}", a , b);
println!("AND: {}", a & b);
println!("OR: {}", a | b);
println!("XOR: {}", a ^ b);
println!("NOT a: {}", !a);
println!("Left shift: {}", a << 2);
println!("Right shift: {}", a >> 1);
}
output :-
Operand 1: 5, Operand 2: 6
AND: 4
OR: 7
XOR: 3
NOT a: -6
Left shift: 20
Right shift: 2
Quiz
What is the output of the following code?
fn main() {
let mut a = 1;
let mut b = 2;
a = a & b;
a = a << 1;
b = b >> 3;
println!("a: {}", a);
println!("b: {}", b);
}
A) a: 0
b: 2
B) a: 0
b: 0
C) a: 2
b: 0
D) a: 2
b: 2
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .