Control Visibility Within Different Files Using 'pub'
Control Visibility Within Different Files Using ‘pub’
When modules get large and become cumbersome to store in a single file, it is possible to move their definitions to a separate file to make the code easier to navigate. It is possible to access a module even if it belongs to a different file. To use the module in a different file, write mod followed by the name of the file in which the module is declared.
- Implicit Declaration A block of code put in a file without wrapping in a mod block implicitly declares a module.
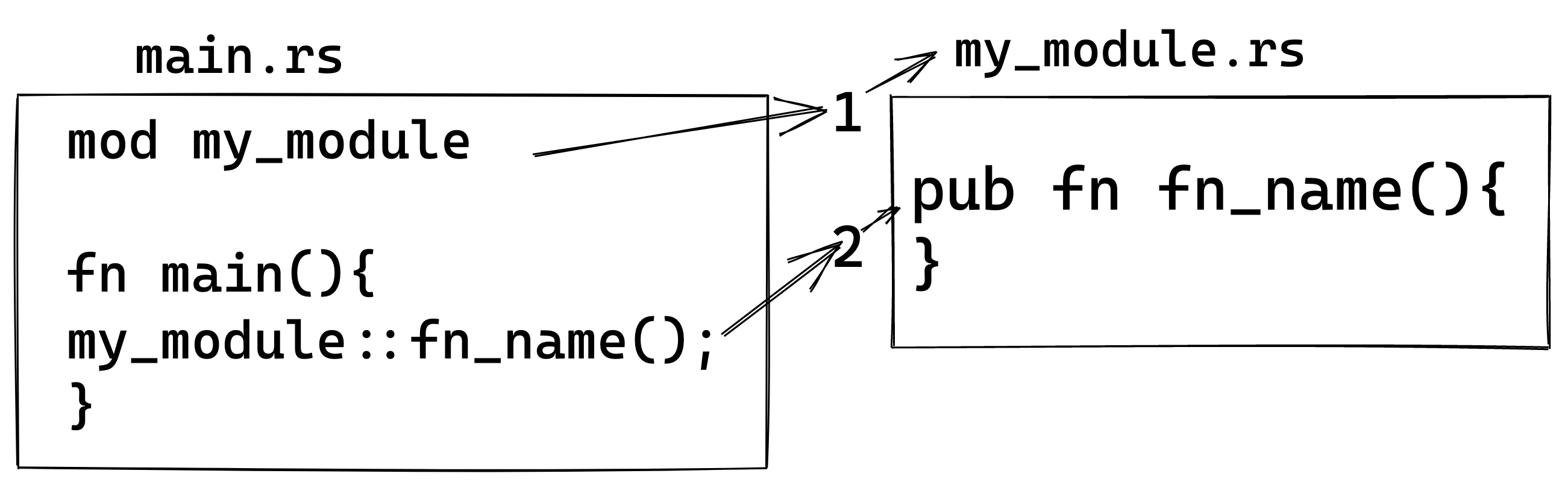
- Import the module
mod file_name
- Call the module
file_name::x
Where x can be any construct within the module, i.e., function, array, trait, struct.
📝 Rust code is always put in files with .rs extension
Explicit Declaration
The code in a file is wrapped within the mod block. This explicitly declares a module.
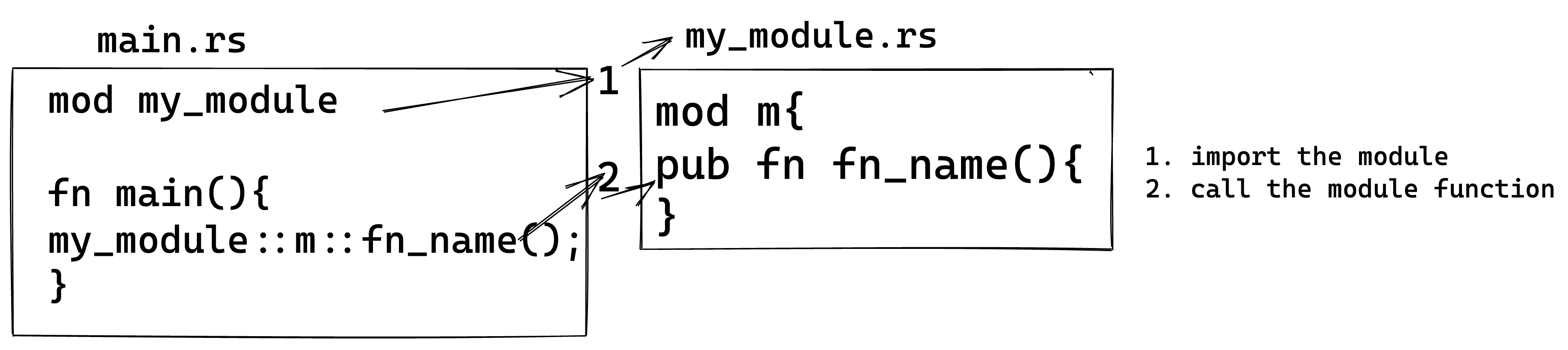
- Import the module
mod file_name
- Call the module
file_name::module_name::x
where x can be any construct within the module, i.e., function, array, trait, struct.
Privacy Rule
- If the module belonging to some other file is to be made accessible then it should be made public by using the pub keyword before the mod.
📝Once the module is made public using pub, all privacy rules for defining modules within the same file apply.
Example
The following example shows how a module in another file can be accessed.
- Implicit declaration
The following example declares a module implicitly in a file
my_mod.rsand calls it frommain.rs. Note: In implicit declaration modules are public by default
main.rs
mod my_mod;
fn main() {
println!("Invoke function in my_mod.rs");
my_mod::my_public_function();
}
my_mod.rs
// declare a module
pub fn my_public_function() {
println!("I am a public function in my_mod.rs");
}
output
Invoke function in my_mod.rs
I am a public function in my_mod.rs
Explicit declaration
- The following example declares a module module in a file
my_mod.rsand call it frommain.rs.
main.rs
mod my_mod;
fn main() {
println!("I am a public function in my_mod.rs");
my_mod::module::my_public_function();
}
my_mod.rs
// declare a module
pub mod module{
pub fn my_public_function() {
println!("I am a public function in my_mod.rs");
}
}
output
I am a public function in my_mod.rs
I am a public function in my_mod.rs
Quiz
Test your understanding of modules in different files.
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .