If Expression
If Expression
There can be multiple conditional constructs using an if statement.
If expression
If…else expression
If…else if…else expression
Nested if expression
Shorthand if expression
Let’s discuss each one of them in detail:-
If Expression
If expression takes a condition. If the condition within the if expression evaluates to be true, then the block of code is executed.
- Syntax The general syntax is:
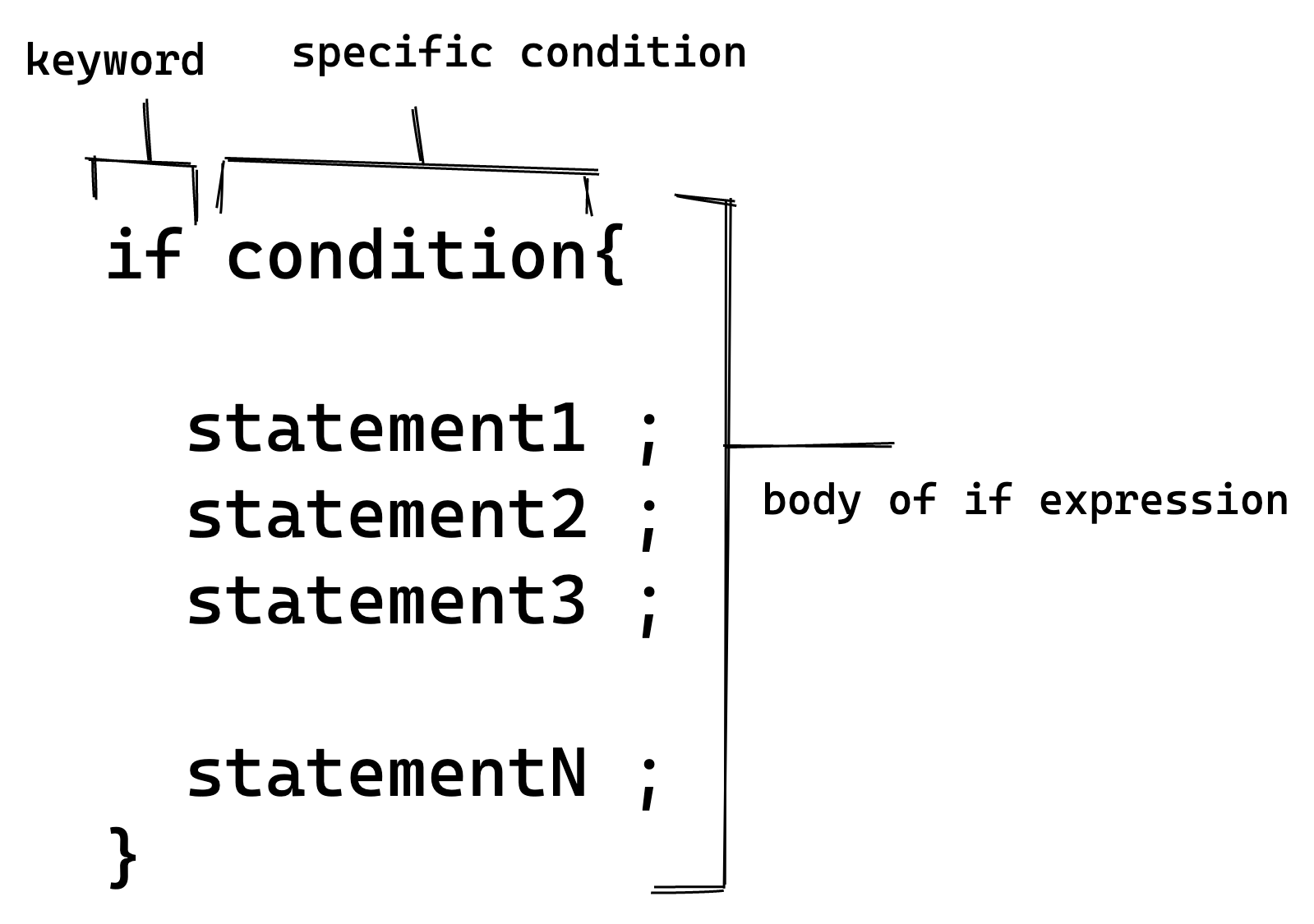
Illustration
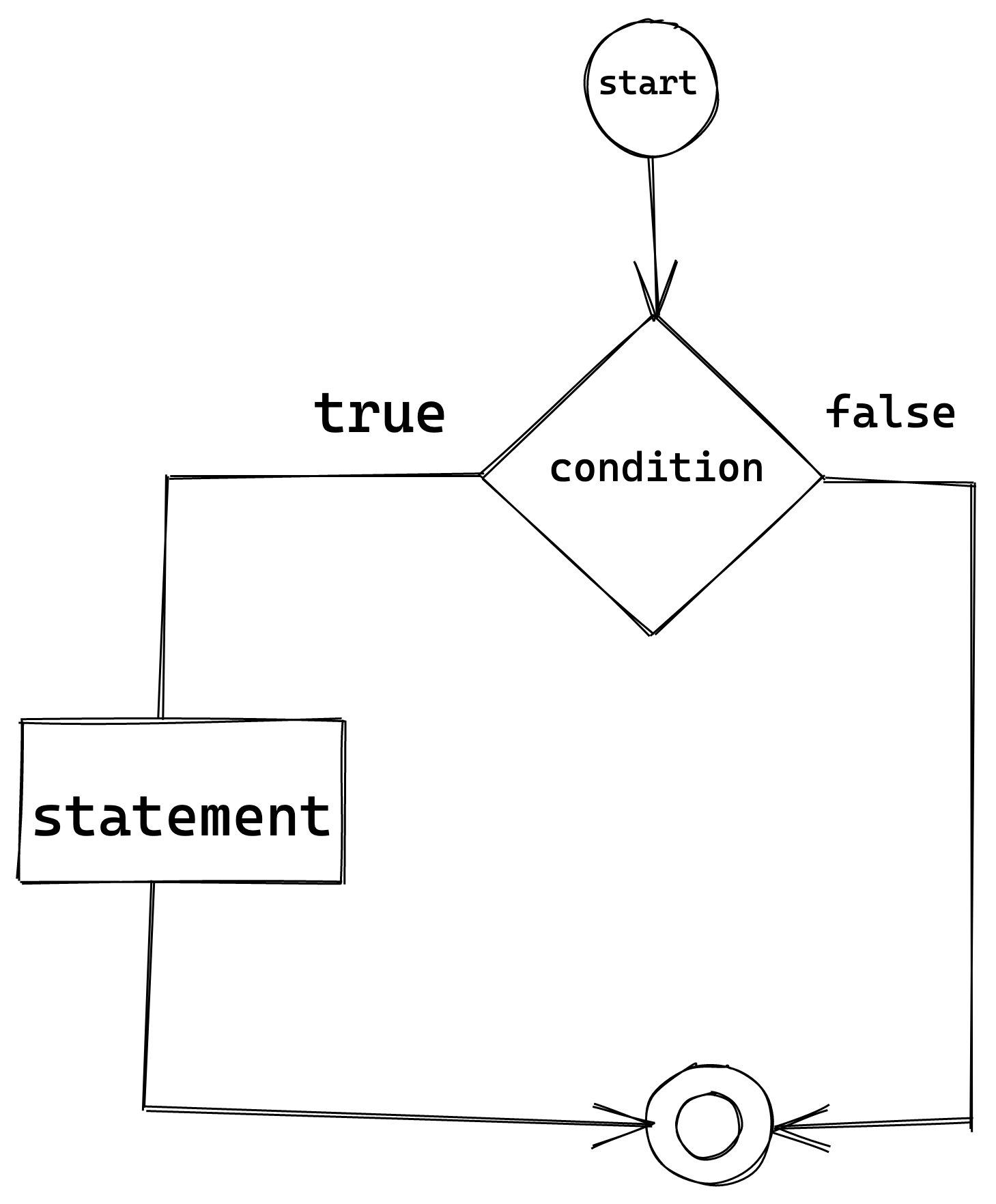
The following flow chart explains the concept of an if statement:
fn main() {
//define a variable
let learn_language = "Rust";
// if construct
if learn_language == "Rust" {
println!("You are learning Rust language!");
}
}
output:-
You are learning Rust language!
If…else Expression
In an if..else construct, if the condition within the if expression evaluates to be false, then the statement within the else block is executed.
- Syntax
The general syntax is:
Illustration
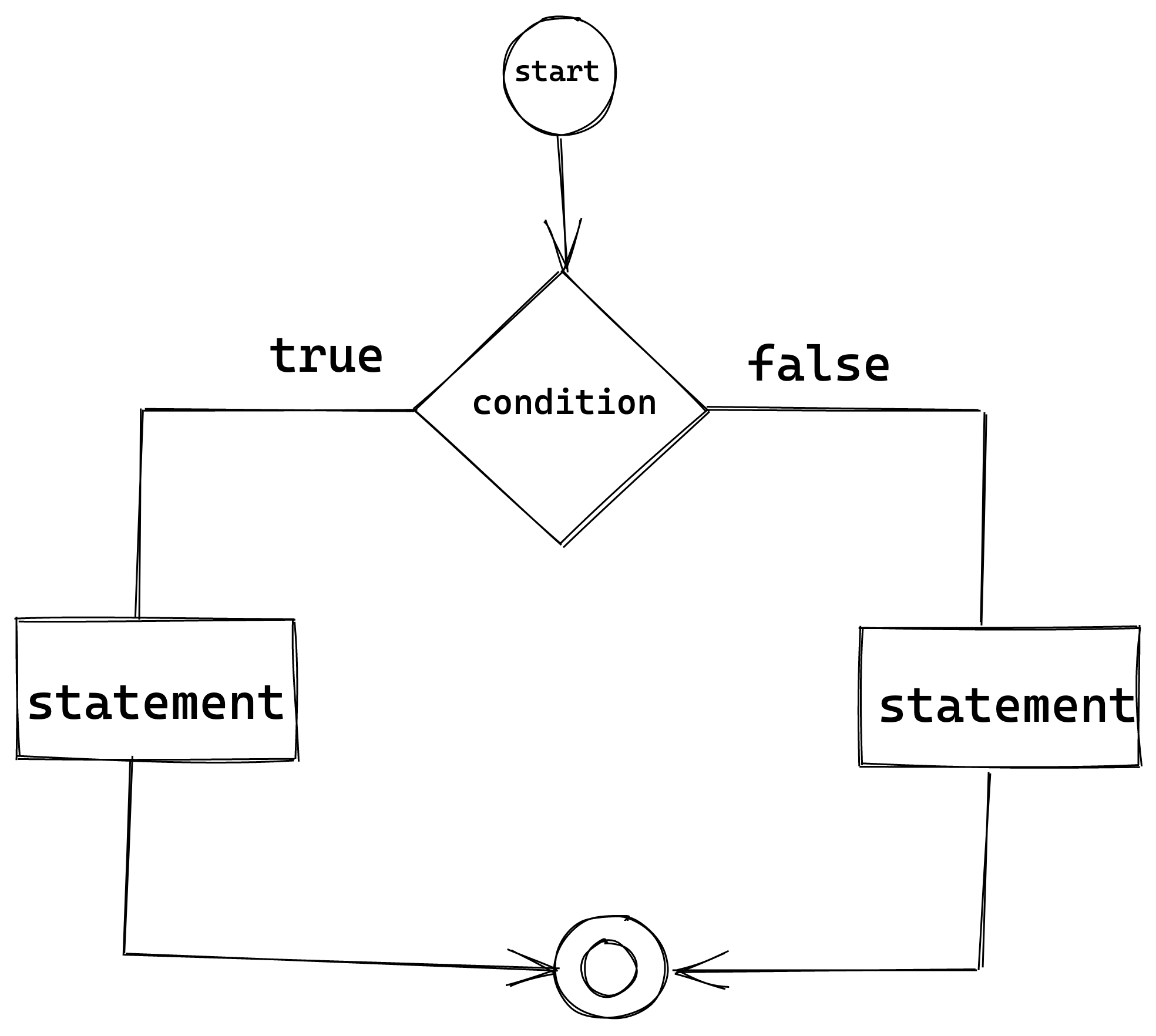
The following flow chart explains the concept of an if..else statement:
fn main() {
//define a variable
let learn_language = "Rust";
// if else construct
if learn_language == "Rust" {
println!("You are learning Rust language!");
}
else {
println!("You are learning some other language!");
}
}
Output
You are learning Rust language!
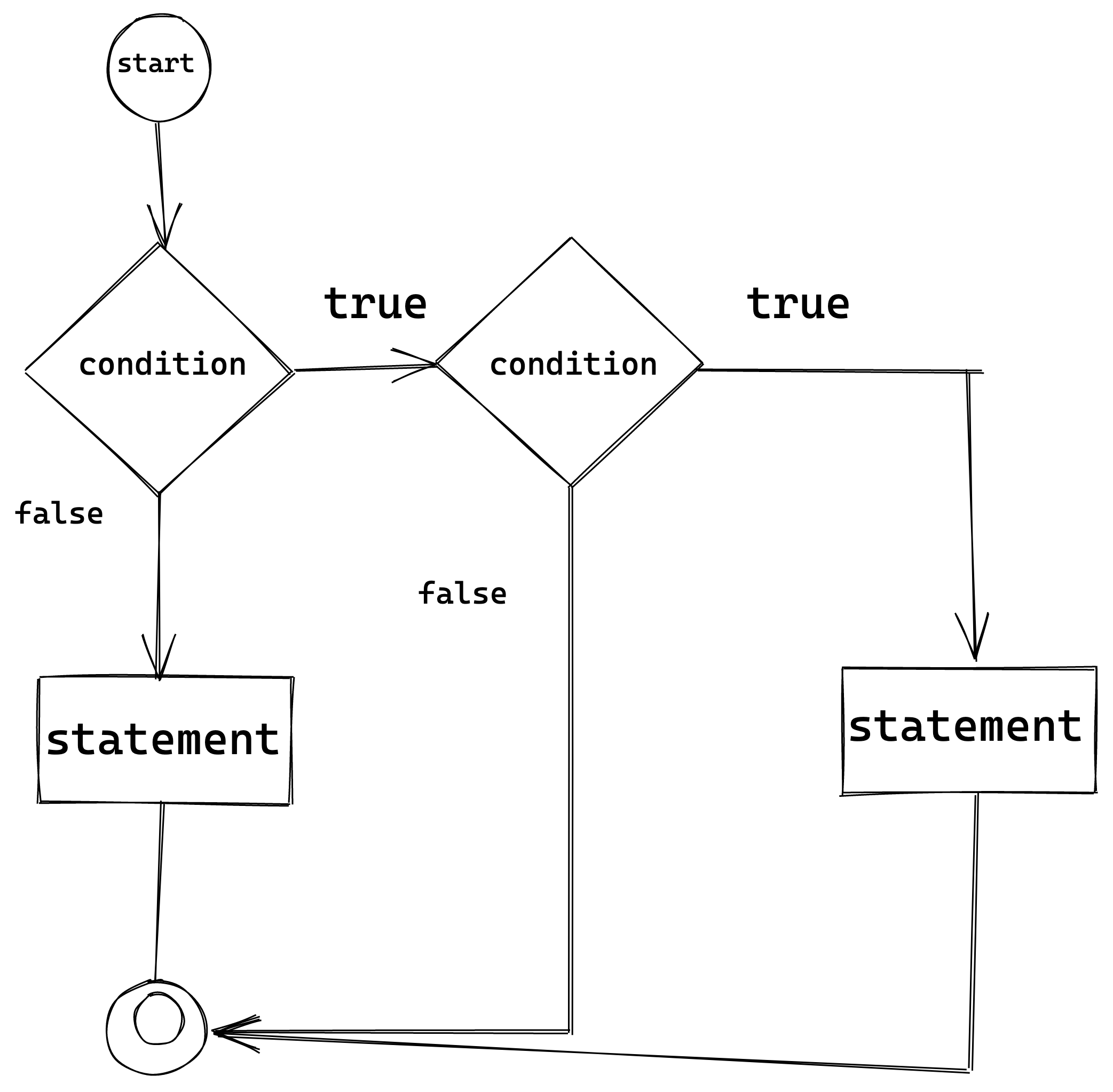
if…else if…else Expression
If there are multiple conditions to be checked, then if..else if..else construct is used.
Syntax The general syntax is:
llustration
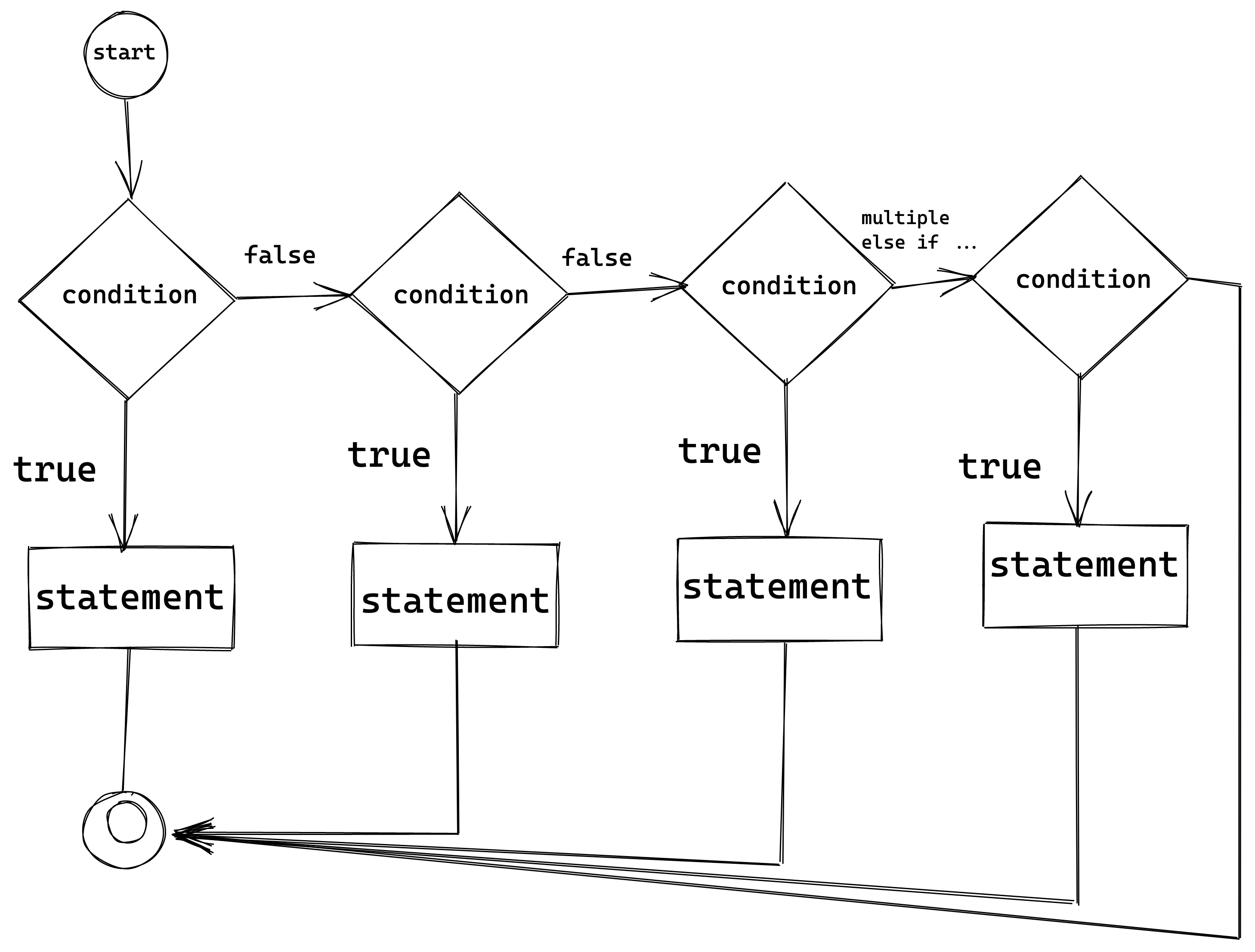
The following flow chart explains the concept of an if..else if..else expression:
fn main() {
//define a variable
let learn_language="Rust";
// if..elseif..else construct
if learn_language == "Rust" {
println!("You are learning Rust language!");
}
else if learn_language == "Java" {
println!("You are learning Java language!");
}
else {
println!("You are learning some other language!");
}
}
Output
You are learning Rust language!
Nested if Expression
An if expression inside the body of another if expression is referred to as a nested if expression.
- Syntax
An if construct is enclosed within an if construct.
The general syntax is:
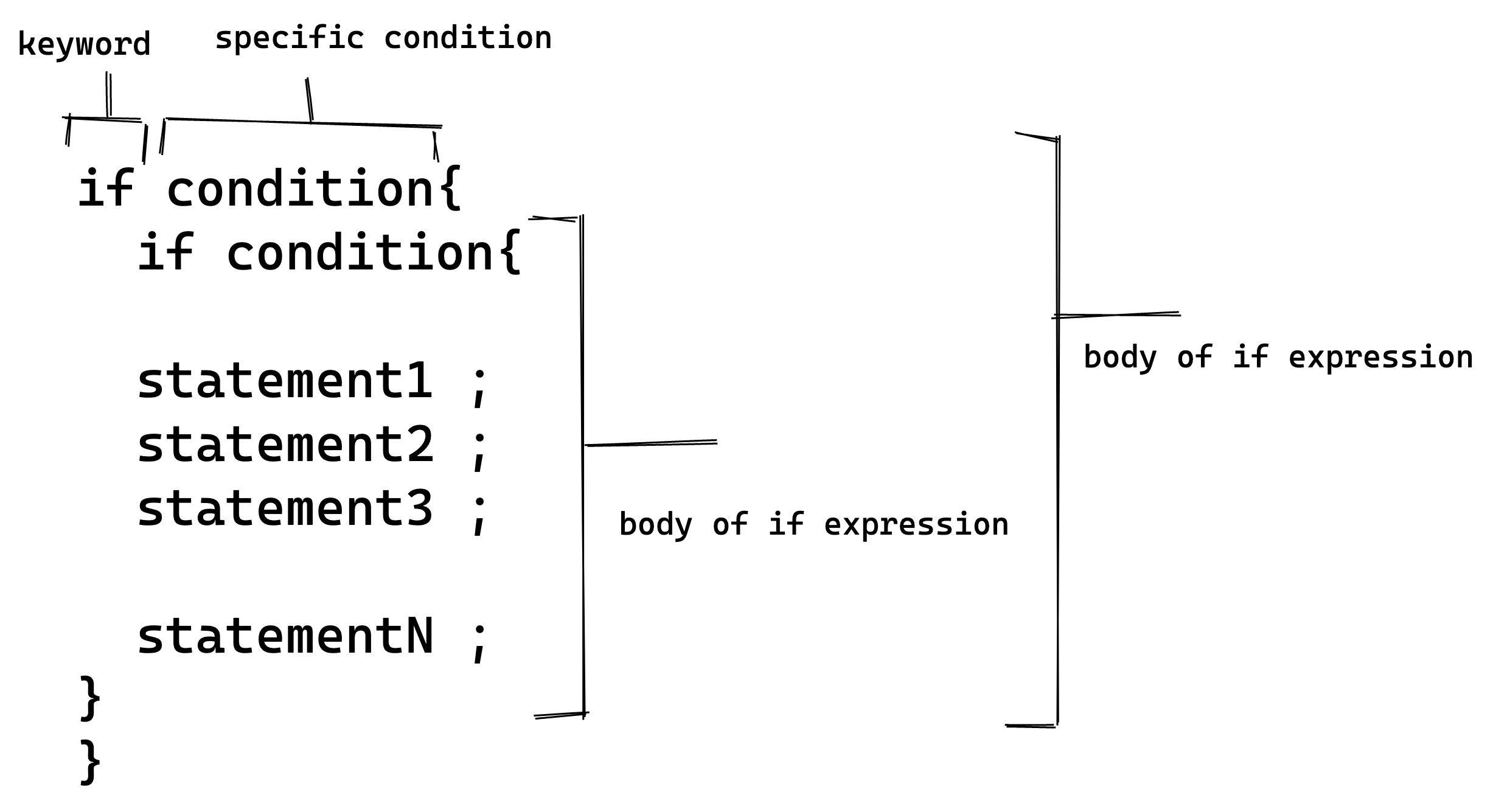
Note: The nested if expression can also be written with a AND expression in an if.
if condition1 && condition2
{
//statement
}
This is true only if the second if statement is the only thing inside the first if.
Illustration
The following flow chart explains the concept of a nested if statement .
Note: There can be as many levels of nesting as you want.
fn main() {
//define a variable
let learn_language1 = "Rust";
let learn_language2 = "Java";
// outer if statement
if learn_language1 == "Rust" { // inner if statement
if learn_language2 == "Java"{
println!("You are learning Rust and Java language!");
}
}
else {
println!("You are learning some other language!");
}
}
output:-
You are learning Rust and Java language!
Shorthand if
Instead of writing a lengthy if-else construct, we can use a shorthand if.
Syntax
The general syntax is:
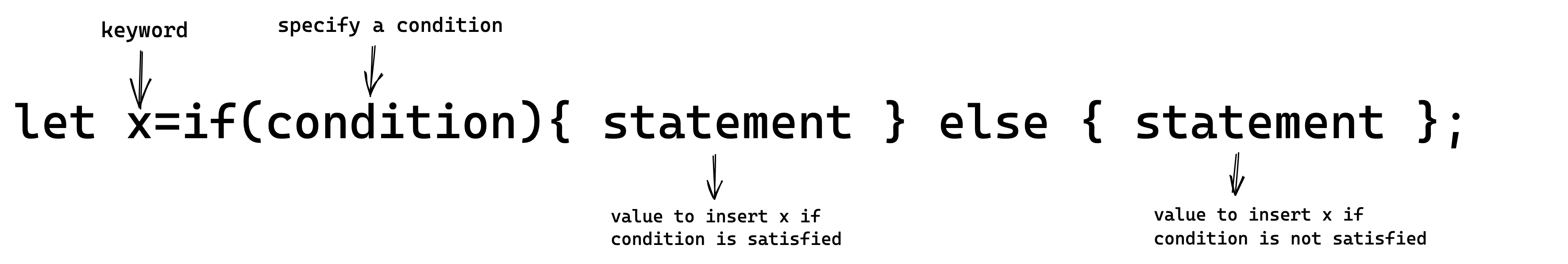
Note: This is similar to a ternary operator in languages like C and C++.
fn main() {
//define a variable
let learn_language = "Rust";
// short hand construct
let res= if learn_language == "Rust" {"You are learning Rust language!"} else {"You are learning some other language!"};
println!("{}", res);
}
Note: Expressions can return a value, unlike statements. Recall that the semicolon turns any expression into a statement. It throws away its value and returns a unit () instead.
fn main() {
let x = "Rust";
let y: bool = if x == "Rust" { true } else { false };
// let z: bool = if x == "Rust" { true; } else { false; };
println!("x:{}", x);
println!("y:{}", y);
}
Note: Uncommenting line 6 in the above code gives an error ❌ since we are trying to convert an expression to a statement and hence not returning a value.
Quiz
You are allowed to play
The sport is Baseball - [ ] Age is greater than 21
You are allowed to play
The sport is Tennis
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .