Introduction to Vectors
Introduction to Vectors
- What are Vectors?
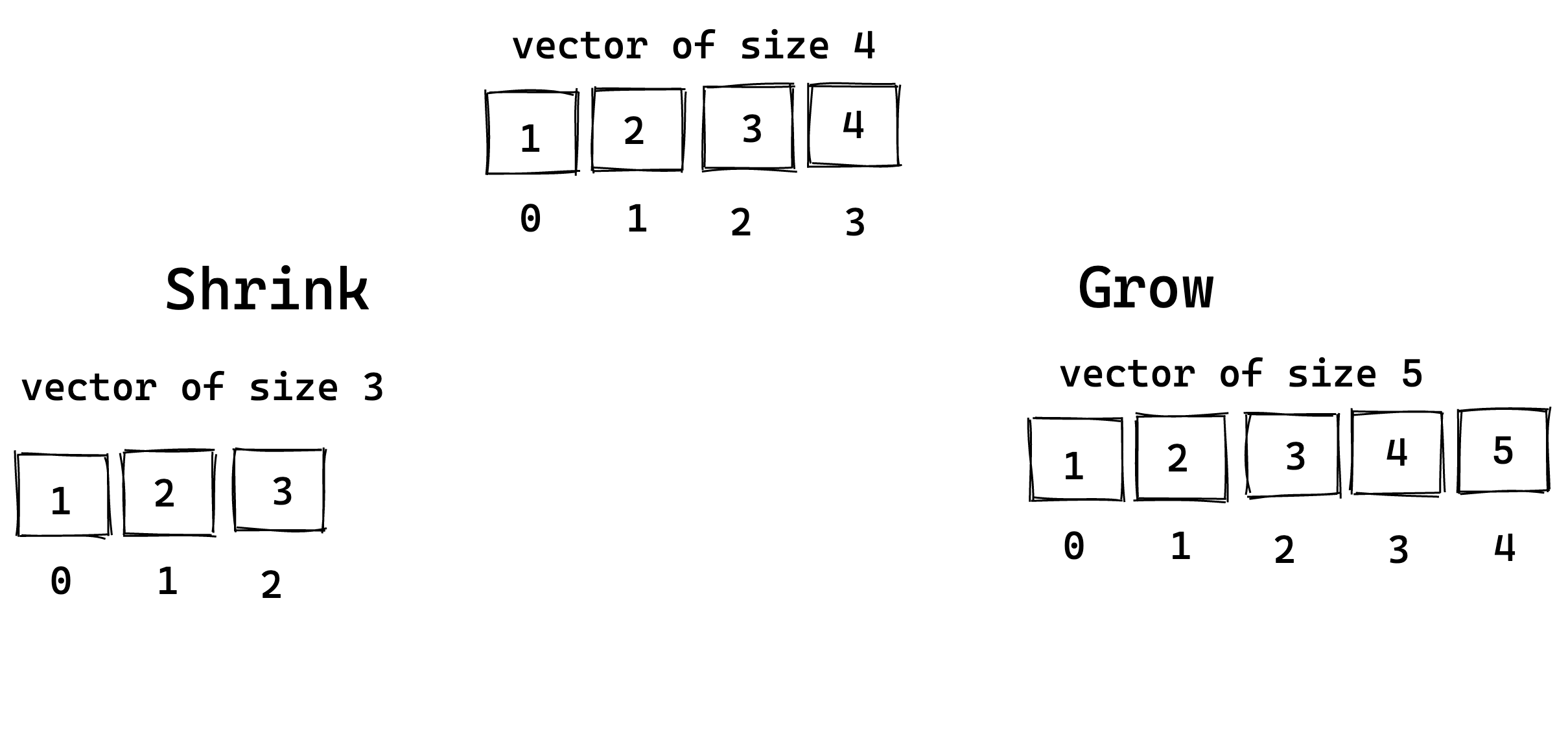
Vectors are resizable arrays meaning(they can grow or shrink in size).
Create Vectors
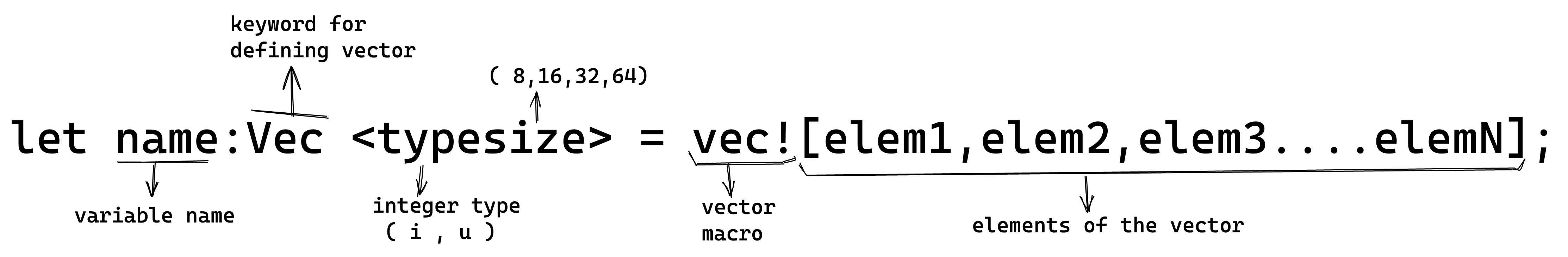
There are two ways to create a vector:
Syntax
- To create a vector write the vector macro
(vec!)followed by the elements of the vector enclosed in square brackets
- To create a vector write the vector macro

It is optional to define the type and size of the vector enclosed within angular brackets.
Use the vector macro(vec!) before defining the elements of the vector.
fn main() {
//define a vector of size 4
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
//print the vector
println!("{:?}", my_vec);
}
output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Note: Like arrays can be displayed on the screen using the println!() macro.
Access an Element of a Vector
- Any value of the vector can be accessed by writing the vector name followed by the index number enclosed within square brackets
[ ].
fn main() {
//define a vector of size 4
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
//access a particular value
println!("{}", my_vec[0]);
}
output
1
Note: If you try to access an index that does not exist, the compiler will give out of bound access error, ❌.
This is illustrated in the code below:
fn main() {
//define a vector of size 4
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
//access a particular value
eprintln!("{}", my_vec[9]);
}
output
thread 'main' panicked at 'index out of bounds: the len is 5 but the index is 9', /rustc/73528e339aae0f17a15ffa49a8ac608f50c6cf14/src/libcore/slice/mod.rs:2796:10
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace.
To cater to out of bound exceptions, you can use a None keyword.
fn main() {
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3,4,5];
match my_vec.get(9) {
Some(x) => println!("Value at given index:{}", x),
None => println!("Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound")
}
}
output
Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound
Print the Vector
fn main() {
println!("Print using debug trait");
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3,4,5];
//using debug trait
println!("Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
println!("Print using for loop");
// using loop
let mut index = 0;
for i in my_vec {
println!("Element at index {}:{} ", index, i);
index = index+1;
}
}
output
Print using debug trait
Vector : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Print using for loop
Element at index 0:1
Element at index 1:2
Element at index 2:3
Element at index 3:4
Element at index 4:5
Methods of Vectors
The methods of vectors are summarized in the chart below:
| # | method | explaination |
|---|---|---|
1 | Vec::new() | creates a new vector |
| 2 | .push() | push a value |
| 3 | .pop() | pop a value |
| 4 | .contains() | returns true if the vector contains a particular value |
| 5 | remove(i) | remove value at given index |
| 6 | .len() | return len of the vector |
The following code demonstrates each of the above methods:
fn main() {
let mut my_vec = Vec::new();
println!("Empty Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
my_vec.push(1);
my_vec.push(2);
my_vec.push(3);
println!("Pushed elements 1 , 2 , 3 : {:?}", my_vec);
my_vec.pop();
println!("Popped value: {}", 3);
println!("Popped element at last index : {:?}", my_vec);
my_vec.remove(1);
println!("Removed value: {}", 2);
println!("Removed element at index 1 : {:?}", my_vec);
println!("Size of vector is :{}", my_vec.len());
println!("Does my vector contains 1 : {}", my_vec.contains(&1));
}
output
Empty Vector : []
Pushed elements 1 , 2 , 3 : [1, 2, 3]
Popped value: 3
Popped element at last index : [1, 2]
Removed value: 2
Removed element at index 1 : [1]
Size of vector is :1
Does my vector contains 1 : true
Note: When using the .contains function, consider borrowing the value.
Quiz
Test your understanding of basics of vectors in Rust.
- [ ] True - [ ] False # What is the output of the following code? ``` fn main() { let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; match my_vec.get(10) { Some(x) => println!("Value at given index:{}", x), None => println!("Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound") } match my_vec.get(3) { Some(x) => println!("Value at given index:{}", x), None => println!("Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound") } } ``` - [ ] ``` Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound Value at given index: 4 ``` - [ ] ``` Value at given index: 4 Sorry, you are accessing a value out of bound ```
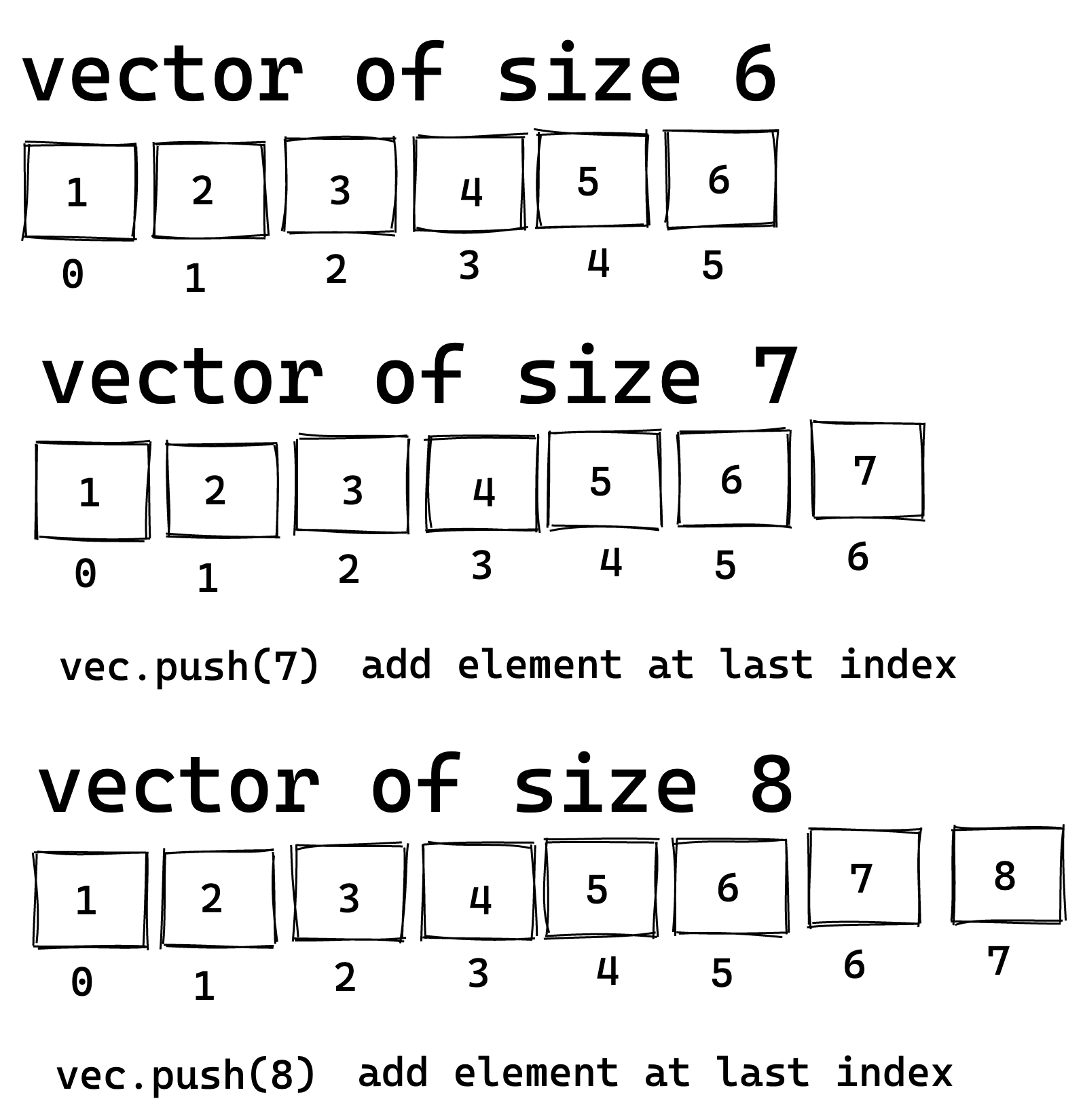
Resizing a Vector
- Add Elements to the Vector
- Define a mutable vector variable.
- To add elements to the vector, use the push method.
The following illustration shows how the size of the vector grows by adding an element:
fn main() {
// define a vector of size 5
let mut my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// print vector
println!("Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
// print the capacity of vector
println!("Capacity of vector: {}", my_vec.capacity());
// print the length of vector
println!("Length of the vector : {}",my_vec.len());
my_vec.push(6);
my_vec.push(8);
// print vector
println!("Vector : {:?}",my_vec);
// print the capacity of vector
println!("Capacity of vector: {}", my_vec.capacity());
// print the length of vector
println!("Length of the vector : {}", my_vec.len());
}
output
Vector : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Capacity of vector: 5
Length of the vector : 5
Vector : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8]
Capacity of vector: 10
Length of the vector : 7
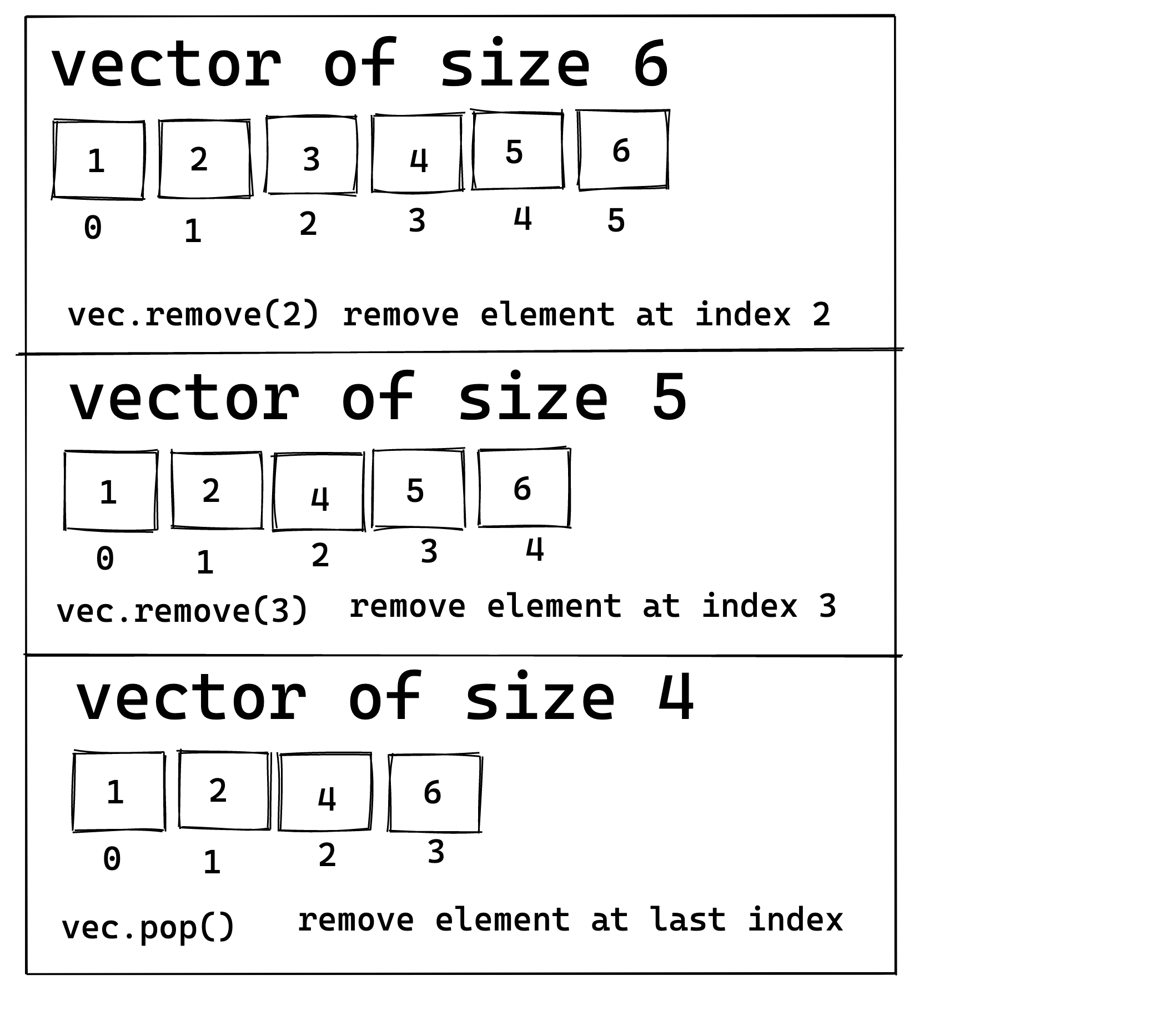
Remove Elements from the Vector
- Define a mutable vector variable.
- Elements can be removed from the tail or at specific index of the vector.
- To remove elements from the tail of the vector, use the pop method.
- To remove elements at a specific position of the vector, specify the index number within the
remove()method.
fn main() {
// define a vector of size 5
let mut my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// print vector
println!("Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
// print the capacity of vector
println!("Capacity of vector: {}", my_vec.capacity());
// print the length of vector
println!("Length of the vector : {}", my_vec.len());
my_vec.pop();
my_vec.pop();
// print vector
println!("Vector : {:?}",my_vec);
// print the capacity of vector
println!("Capacity of vector: {}", my_vec.capacity());
// print the length of vector
println!("Length of the vector : {}", my_vec.len());
}
output:-
Vector : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Capacity of vector: 5
Length of the vector : 5
Vector : [1, 2, 3]
Capacity of vector: 5
Length of the vector : 3
Note that the remove() function requires the index of the vector element to be removed. However, if it is desired to pass the element to be removed,
then we need to know the index of the particular element of the vector and then remove it. Let’s explore that in the next lesson using the .iter() method.
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .