Introduction to Enums
Introduction to Enums
- What Are Enums? Enum is a custom data type that is composed of variants.
Variants are values which are definite.
The key is to enumerate all possible values and select one of the values from the list.
- Let’s consider a real life example to understand the concept of enums. The traffic signal can have
only three possible states: red, yellow and green for stop, slow down, and go respectively.
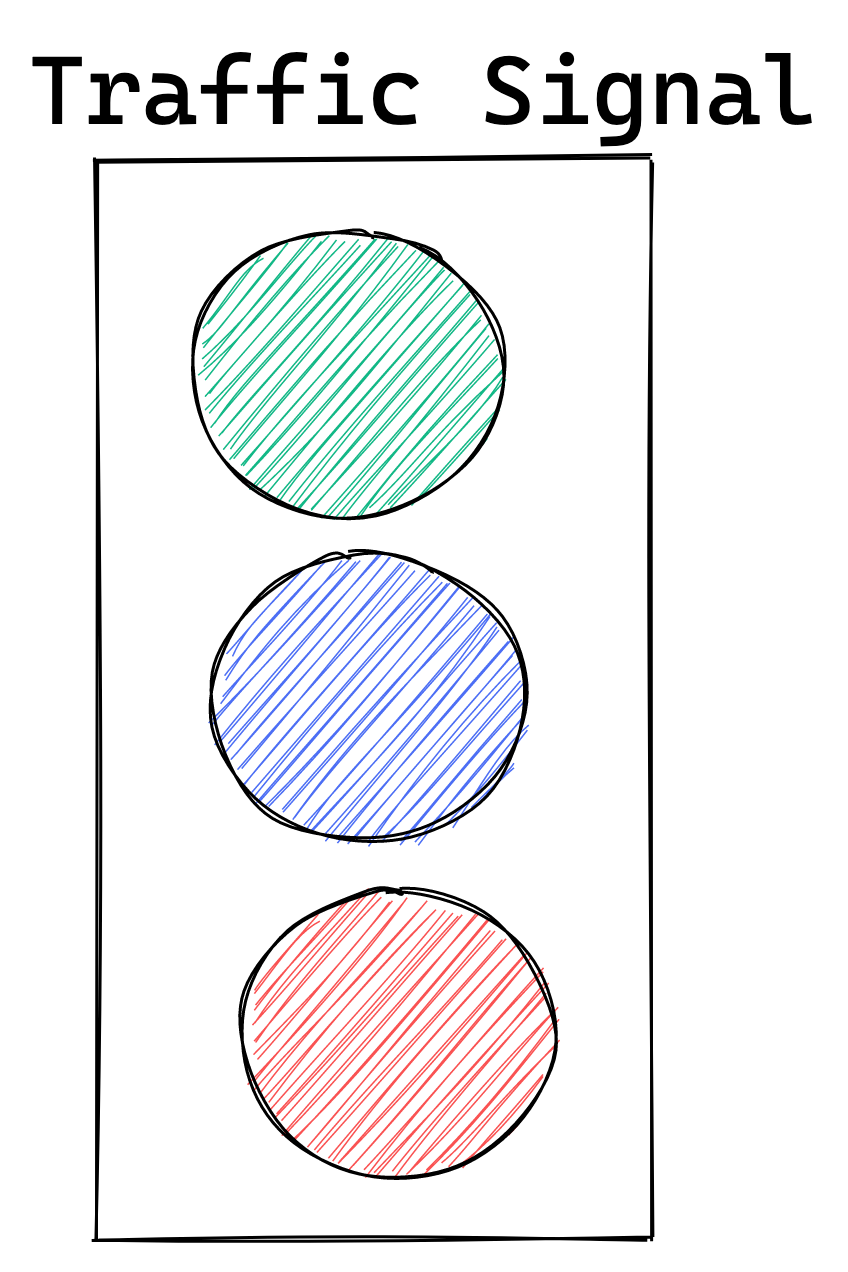
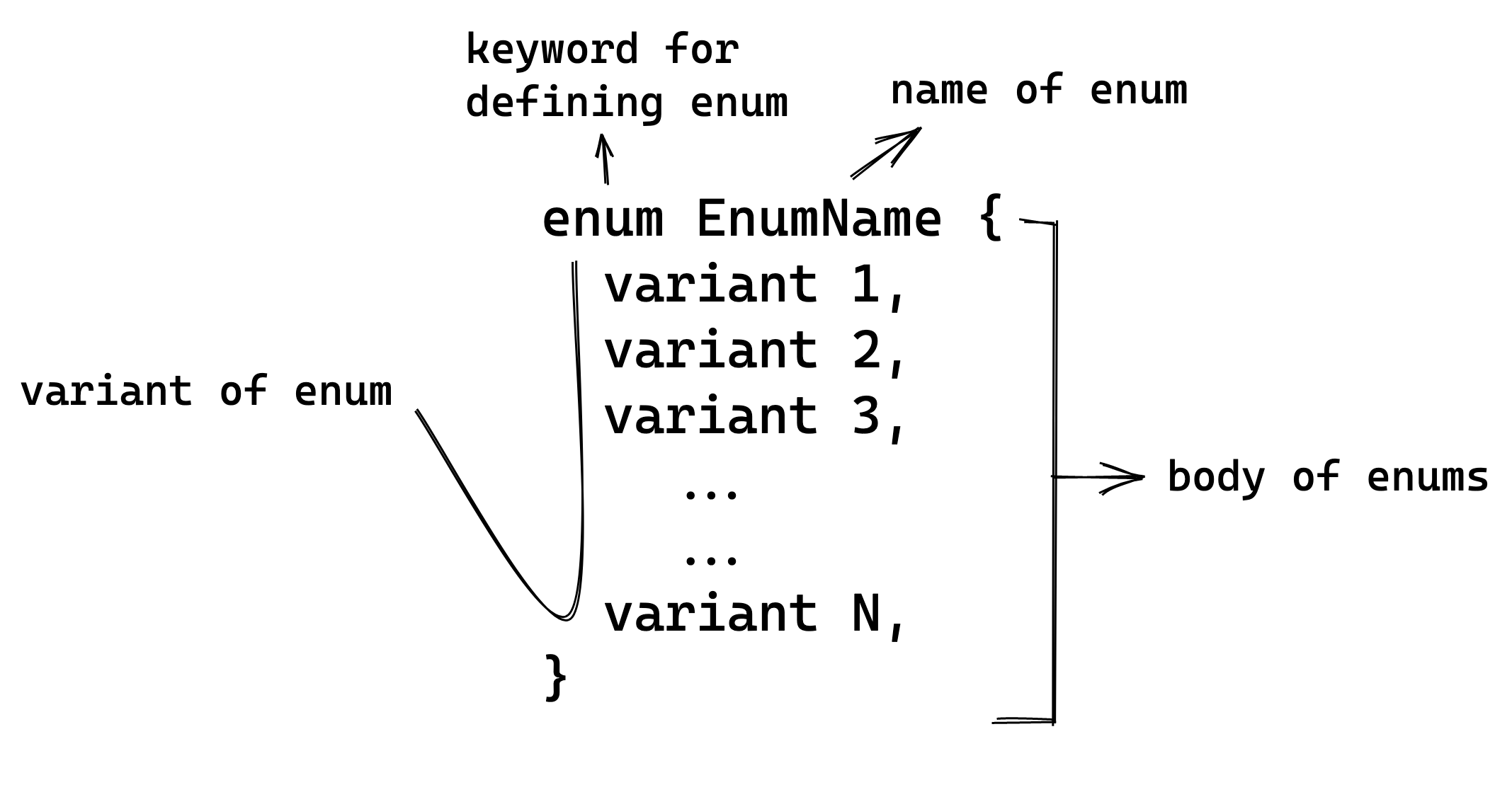
Declare an Enum
Enums are declared using the enum keyword followed by the name of the enum and then the body of the enum
enclosed within curly braces { }. Within the curly braces, the variants of the enum are defined.
Naming Convention
- The name of the enum and it’s variants are written in CamelCase.
Initialize an Enum
Enums are initialized using the name of the enum followed by a double colon(::) and then specifying the name of the variant of the enum.

Note: To print the values of an enum, write #[derive(Debug)] at the beginning of the program code. Use the debug trait{:?} for printing the variants.
- Example
The following example declares an
enumnamedKnightMoves.
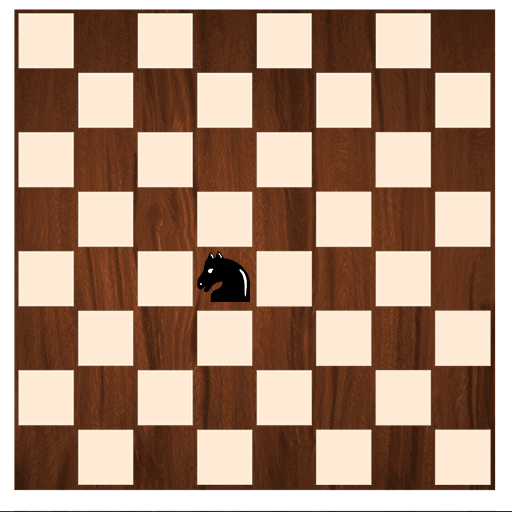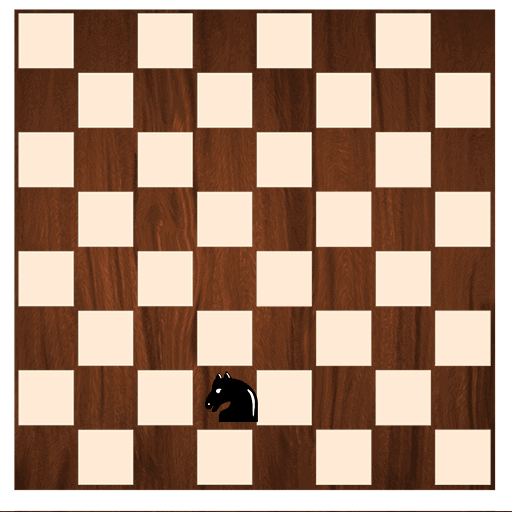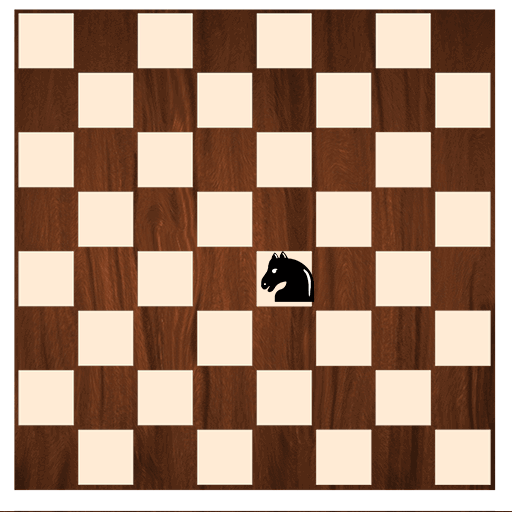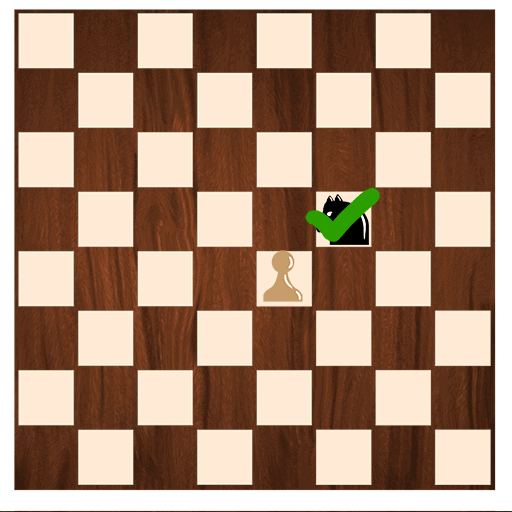
Note: To keep things simple, two variants are mentioned. However, a Knight in chess can move be in four directions. It moves to a square that is two squares away horizontally and one square vertically, or two squares vertically and one square horizontally
// make this `enum` printable with `fmt::Debug`.
#[derive(Debug)]
enum KnightMove{
Horizontal, Vertical
}
fn main() {
// use enum
let horizontal_move = KnightMove::Horizontal;
let vertical_move = KnightMove::Vertical;
// print the enum values
println!("Move 1: {:?}", horizontal_move);
println!("Move 2: {:?}", vertical_move);
}
output
Move 1: Horizontal
Move 2: Vertical
Quiz
Test your understanding of basics of enums in Rust.
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .