Iterating Over a Vector
Iterating Over a Vector
If it is desired to access each element of a vector, then it is possible to iterate over the elements of a vector using iter() rather than using the indexes
to access a particular element of a vector using the square bracket notation
Iterate Using .iter() Built-in Method
we learned to remove an element given an index. However, to remove a particular element, we first need to find the index of that element and then call the remove function passing that index.
For this we can use the
.iter().position(|&e| e == element_name).unwrap().
Here,
iter()is the built-in function that iterates over the elements of the vector..positionis a built-in function that takes the element name to get the position of that element in the vector, i.e.,(|&e| e == element_name)defines a variable e with the value equal to the name of the element that we want to find..unwrap()is the built-in function.
fn main() {
// defines a mutable vector
let mut my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// define the value to be removed
let value = 2;
// get the index of the value in the vector
let index = my_vec.iter().position(|&r| r == value).unwrap();
// call the built-in remove method
my_vec.remove(index);
// print the updated vector
println!("Updated Vector: {:?}", my_vec);
}
output
Updated Vector: [1, 3, 4, 5]
As you can see the value 2 is removed from the vector. you’ll learn how the iterator function helps to loop through each element in the vector index-by-index.
Loop Through the Values
- Define a vector variable.
- The values of the vector within the loop can be traversed using
.iter().
📝If you don’t write .iter() within the loop defination, a simple for loop will give you the same result.
fn main() {
// define a vector of size 5
let my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// using loop
let mut index = 0;
for i in my_vec.iter(){ // it works even if .iter() is not written
println!("Element at index {}:{} ", index, i);
index = index + 1;
}
}
output
Element at index 0:1
Element at index 1:2
Element at index 2:3
Element at index 3:4
Element at index 4:5
Loops and Mutate Values
- Define a mutable vector variable
- The values of the vector within the loop can be changed using
.iter_mut().
fn main() {
// define a vector of size 5
let mut my_vec = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
println!("Initial Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
for x in my_vec.iter_mut(){
*x *= 3;
}
// print the updated vector
println!("Updated Vector : {:?}", my_vec);
}
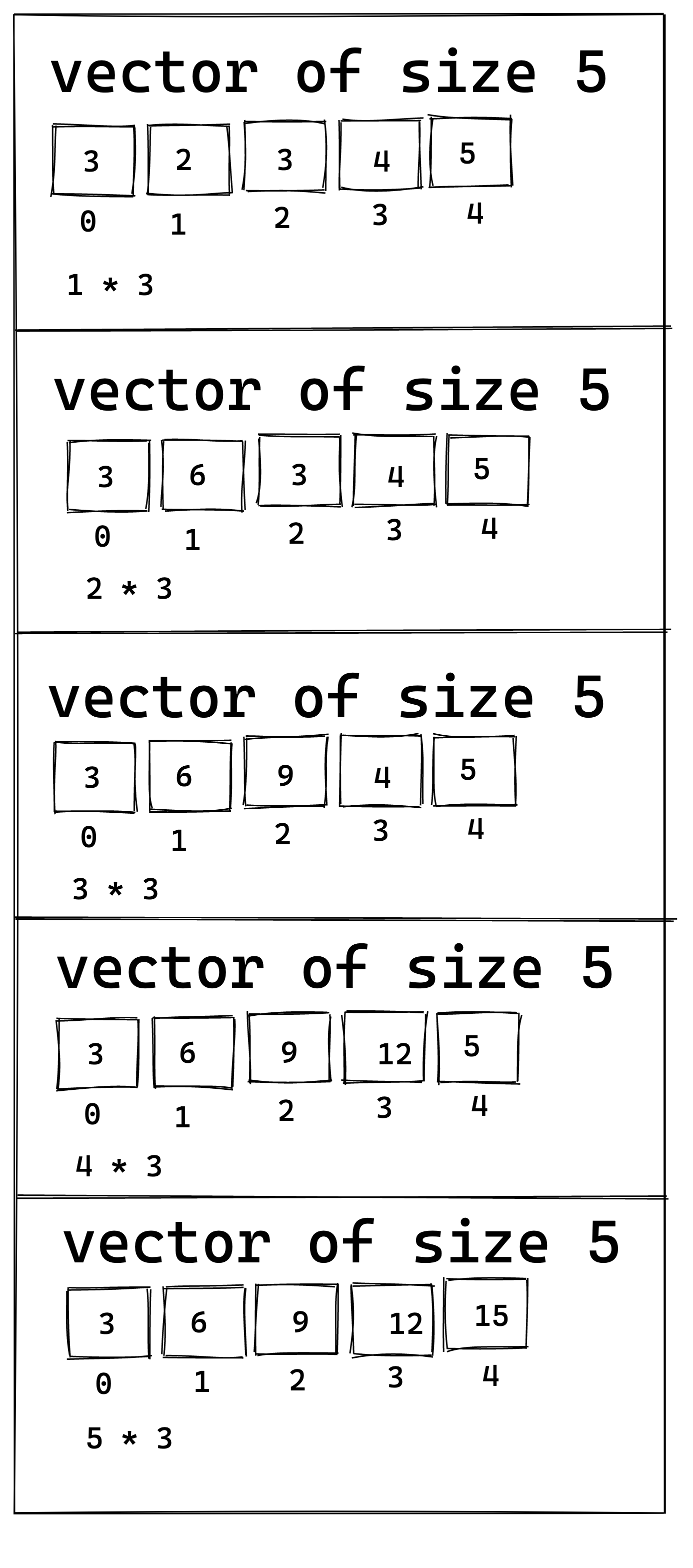
The following illustration shows how the above code works:
Quiz
Test your understanding of looping through a vector in Rust.
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .