Result and Enum
Result and Enum
- What Is Result?
Result is a built-in enum in the Rust standard library. It has two variants Ok(T) and Err(E).
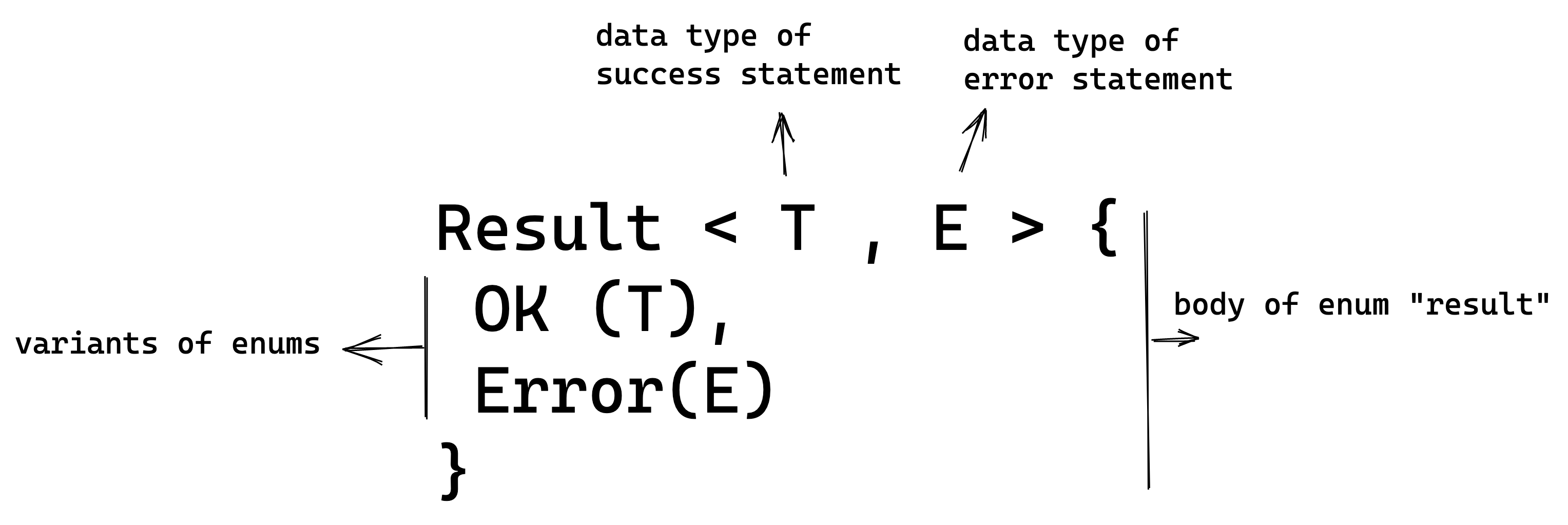
Variants:
Ok(T), returns the success statement of typeTErr, returns the error statement of typeE.
When to Use Result?
- Result should be used as a return type for a function that can encounter error situations. Such functions can return an Ok value in case of success or an Err value in case of an error.
Result and Function
- Using Result as a function return type can be used to return various kinds of success and error codes to let the calling function decode the execution state of the called function.
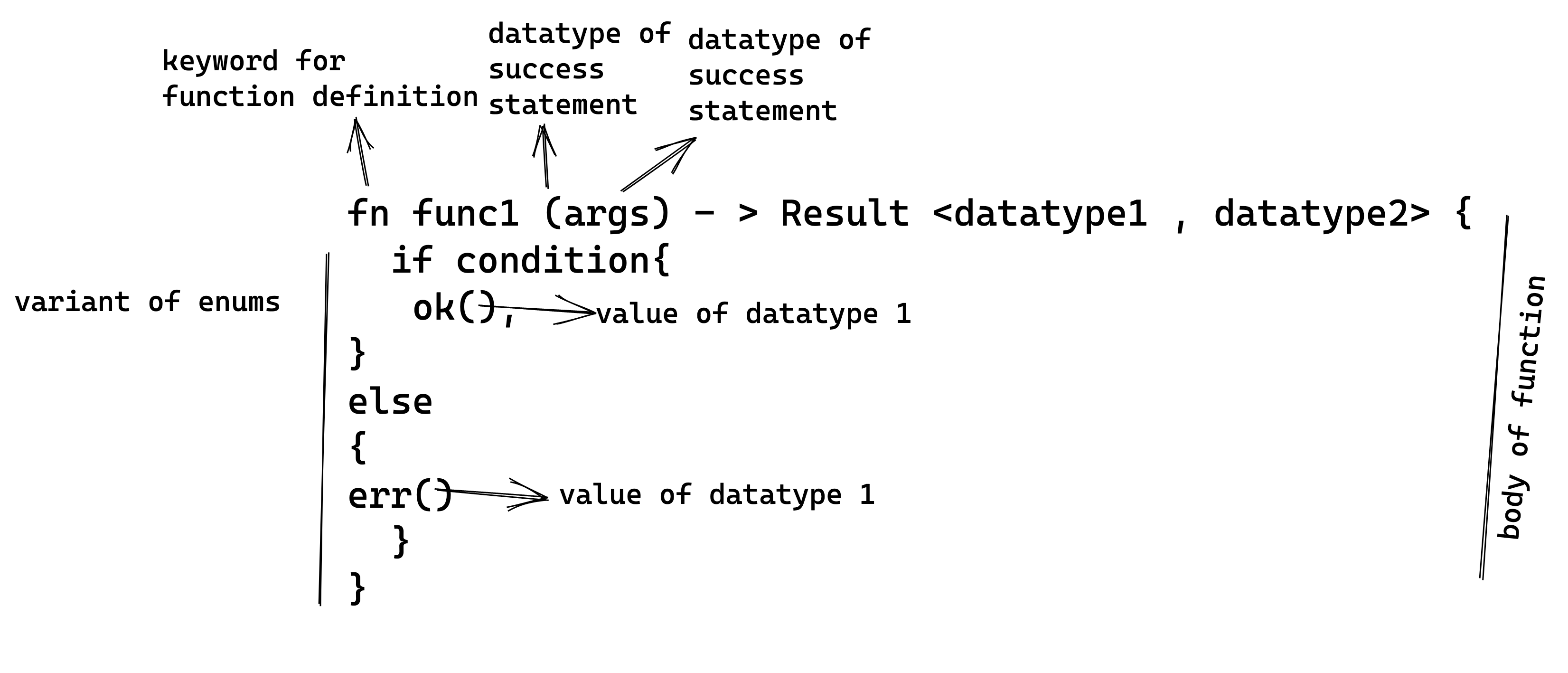
Example 1
The following code has a function file_found which takes a number i and returns a Result of type i32, in case of variant Ok and bool, in case of Err.
fn main() {
println!("{:?}",file_found(true)); // invoke function by passing true
println!("{:?}",file_found(false)); // invoke function by passing false
}
fn file_found(i:bool) -> Result<i32,bool> {
if i { // if true
Ok(200) // return Ok(200)
} else { // if false
Err(false) // return Err(false)
}
}
output
Ok(200)
Err(false)
Example 2 #
The following code has a function divisible_by_3 which takes a number i and returns a Result of type String in case of both variants Ok and Err.
If i is divisible by 3 Ok(Given number is divisible by 3) is returned and Err(Given number is not divisible by 3).
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", divisible_by_3(6)); // invoke function by passing a number 6
println!("{:?}", divisible_by_3(2)); // invoke function by passing a number 2
}
fn divisible_by_3(i:i32)->Result<String,String> {
if i % 3 == 0 { // if number mod 3 equals 0
Ok("Given number is divisible by 3".to_string()) // return this statement
} else { // if if number mod 3 is not equals 0
Err("Given number is not divisible by 3".to_string()) // return this statement
}
}
output
Ok("Given number is divisible by 3")
Err("Given number is not divisible by 3")
is_ok(), is_err() Functions
Rust helps you to check whether the variable of type Result is set to Ok or Err.
fn main() {
let check1 = divisible_by_3(6);
if check1.is_ok(){ // check if the function returns ok
println!("The number is divisible by 3");
}
else{
println!("The number is not divisible by 3");
}
let check2 = divisible_by_3(2);
if check2.is_err(){ // check if the function returns error
println!("The number is not divisible by 3");
}
else{
println!("The number is divisible by 3");
}
}
fn divisible_by_3(i:i32)->Result<String,String> {
if i % 3 == 0 { // check i modulus 3
Ok("Given number is divisible by 3".to_string())
} else {
Err("Given number is not divisible by 3".to_string())
}
}
output
The number is divisible by 3
The number is not divisible by 3
Example 2
The following example uses the assert_eq! macro to check whether the variable value of type Result is set to Ok or Err.
fn main() {
let check1 = divisible_by_3(6);
assert_eq!(check1.is_ok(), true); // left is true and right is true so the assertion passes
let check2 = divisible_by_3(2);
assert_eq!(check2.is_err(), true); // left is true and right is true so the assertion passes
}
fn divisible_by_3(i:i32)->Result<String,String> {
if i % 3 == 0 {
Ok("Given number is divisible by 3".to_string())
} else {
Err("Given number is not divisible by 3".to_string())
}
}
Note: The assertion passes since the expression evaluates to true.
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .