Traits
Traits
When there are multiple different types behind a single interface, the interface can tell which concrete type to access. This is where the traits come in handy.
- What Are Traits?
Traits are used to define a standard set of behavior for multiple structs.
They are like interfaces in Java.
Suppose you want to calculate area for different shapes. We know that the area is calculated differently for every shape. The best solution is to make a trait and define an abstract method in it and implement that method within every struct impl construct.
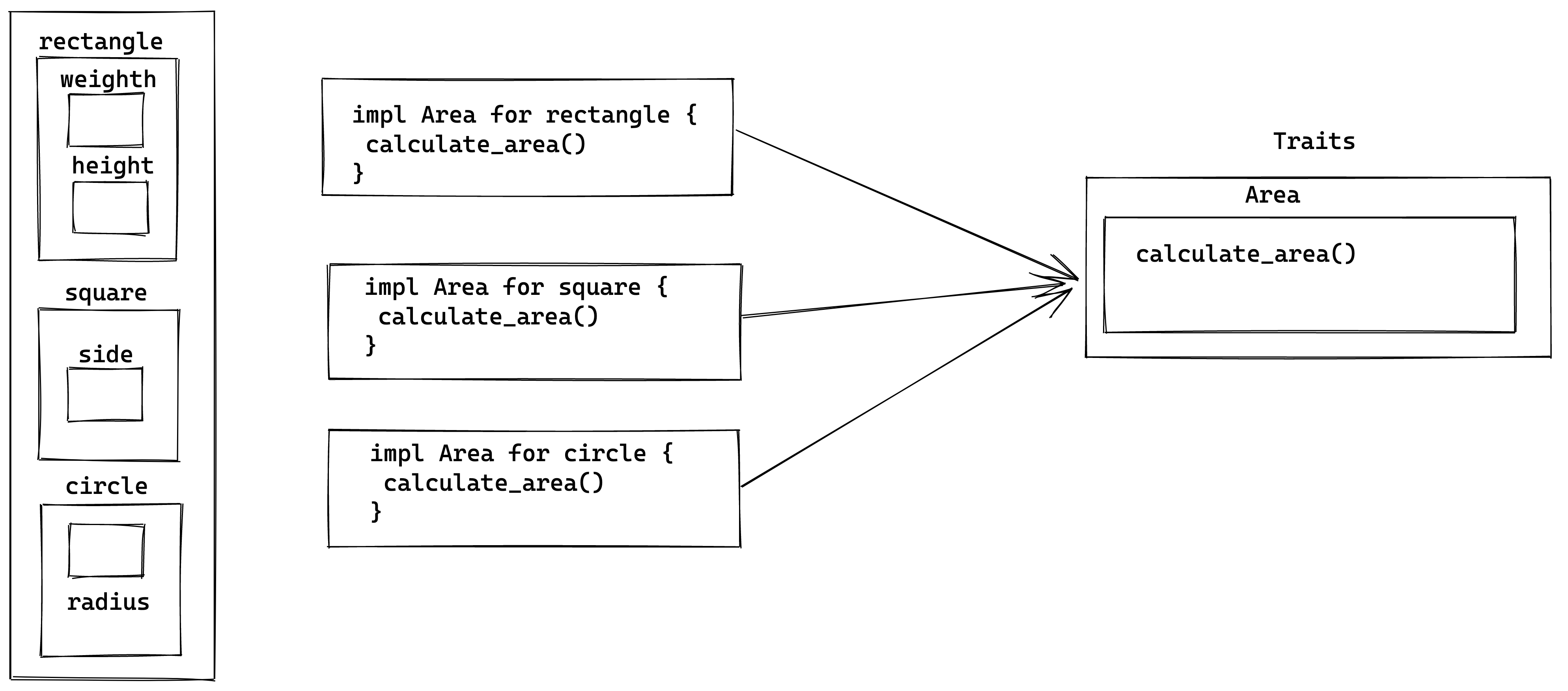
Types of Methods in Traits
There can be two types of methods in traits
- Concrete Method
- The method that has a body meaning that implementation of the method is done within the method.
- Abstract Method
- The method that does not have a body meaning that implementation of the method is done by each struct in its own
implconstruct.
- The method that does not have a body meaning that implementation of the method is done by each struct in its own
Declare a Trait
Traits are written with a trait keyword.

- Naming Convention Name of the trait is written in CamelCase
Implement a trait
Traits can be implemented for any structure.

Example
The following example explains the concept of trait:
fn main(){
//create an instance of the structure
let c = Circle {
radius : 2.0,
};
let r = Rectangle {
width : 2.0,
height : 2.0,
};
println!("Area of Circle: {}", c.shape_area());
println!("Area of Rectangle:{}", r.shape_area());
}
//declare a structure
struct Circle {
radius : f32,
}
struct Rectangle{
width : f32,
height : f32,
}
//declare a trait
trait Area {
fn shape_area(&self)->f32;
}
//implement the trait
impl Area for Circle {
fn shape_area(&self)->f32{
3.13* self.radius *self.radius
}
}
impl Area for Rectangle {
fn shape_area(&self)->f32{
self.width * self.height
}
}
output
Area of Circle: 12.52
Area of Rectangle:4
Quiz
- [ ] abstract - [ ] concrete # Traits are like interfaces in other object oriented languages.
- [ ] True - [ ] False
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .