On this page
article
Type Casting Operator
Type Casting Operator
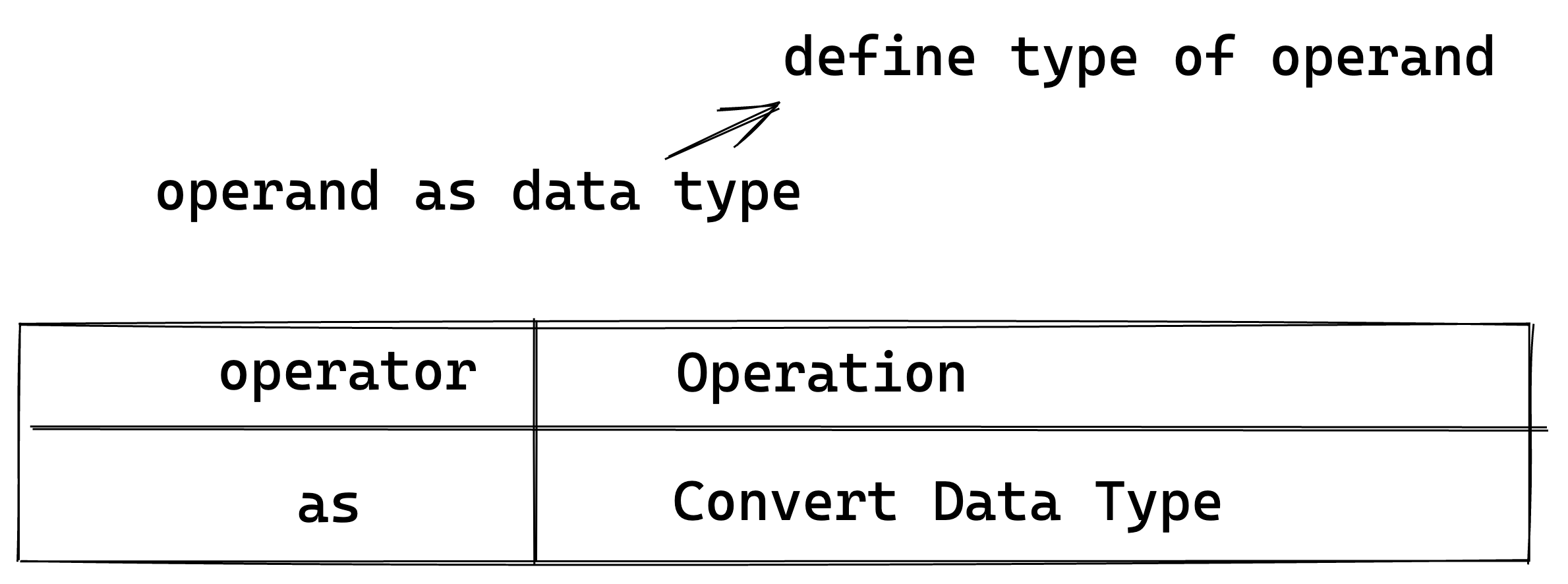
What Is Type Casting? Type casting is when you convert the data type of the variable to some other data type.
- Type Casting in Rust In Rust, typecasting is done using the as keyword followed by the desired data type of the variable or value.
The following example demonstrates the use of type casting operator in a program:
fn main() {
let a = 15;
let b = (a as f64) / 2.0;
println!("a: {}", a);
println!("b: {}", b);
}
output
a: 15
b: 7.5
📝 What data types can be type casted?
- Integer can be type casted to floating-point and vice versa.
- Integer can be typecasted to String
📝What data types cannot be type casted?
- String (&str) or character cannot be type casted to the data type of type integer or float.
- Character cannot be type casted to String type and vice versa
The following code gives an error, ❌, because of the invalid type casting operation:
fn main() {
let a: char = 'r' ; // cannot be type casted
let b = a as &str ;
println!("a: {}", a);
println!("b: {}", b);
}
Quiz
Test your understanding of type casting in Rust!
---
primaryColor: steelblue
secondaryColor: '#e8e8e8'
textColor: black
shuffleQuestions: false
shuffleAnswers: true
locale: en
---
Test your understanding of the assignment and compound assignment operators in Rust.
## What is the output of the following code?
```
fn main() {
let a = 15;
let b = (a as f32) / 3.0; // 5
println!("a:{}",a);
println!("b:{}",b);
}
```
- [ ] ```
a:15
b:7.5
```
- [ ] ```
a:15
b:5
```
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .