Indefinite Loop - While and Loop
Indefinite Loop - While and Loop
- While loop
While loop also iterates until a specific condition is reached. However, in the case of a while loop, the number of iterations is not known in advance.
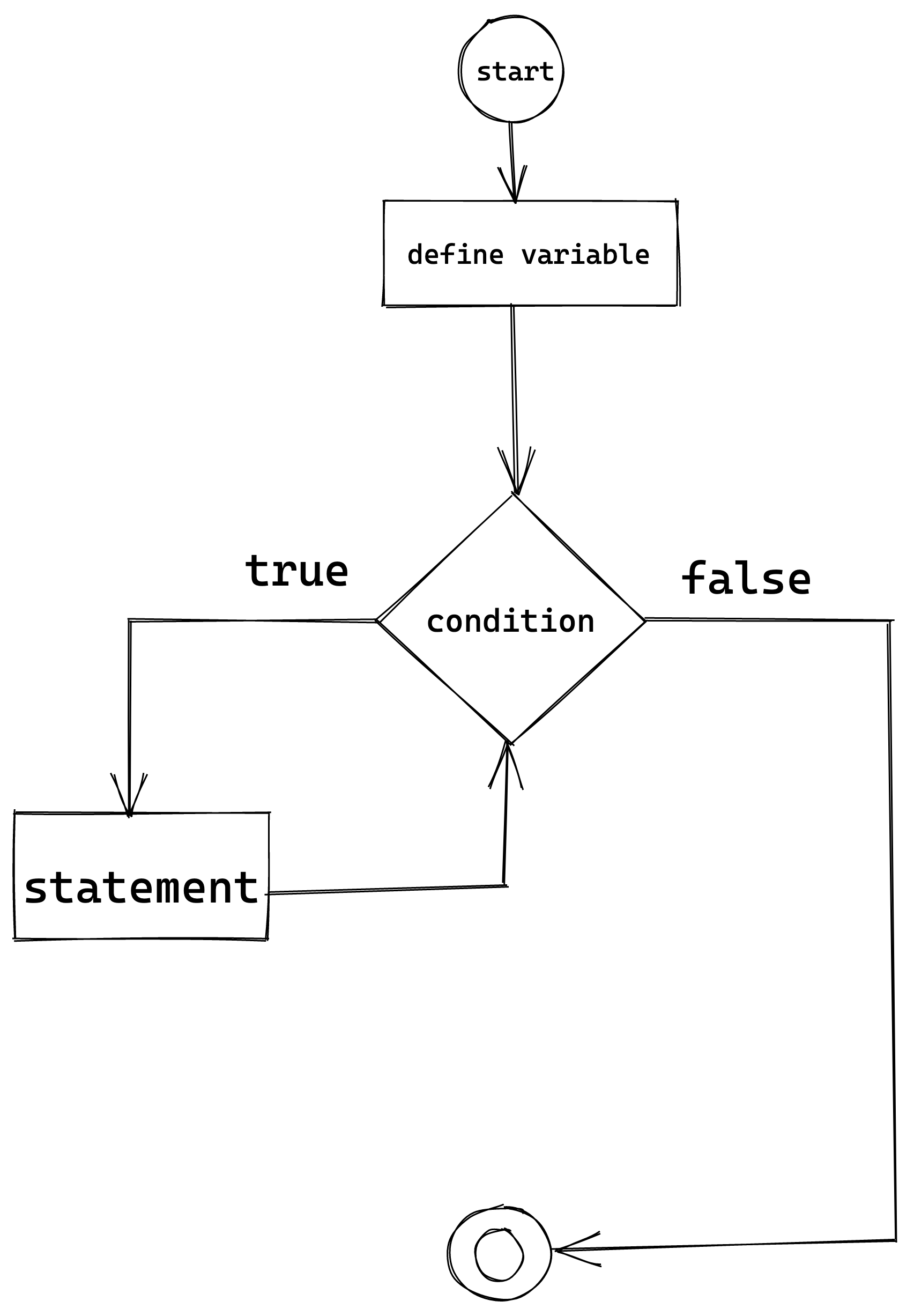
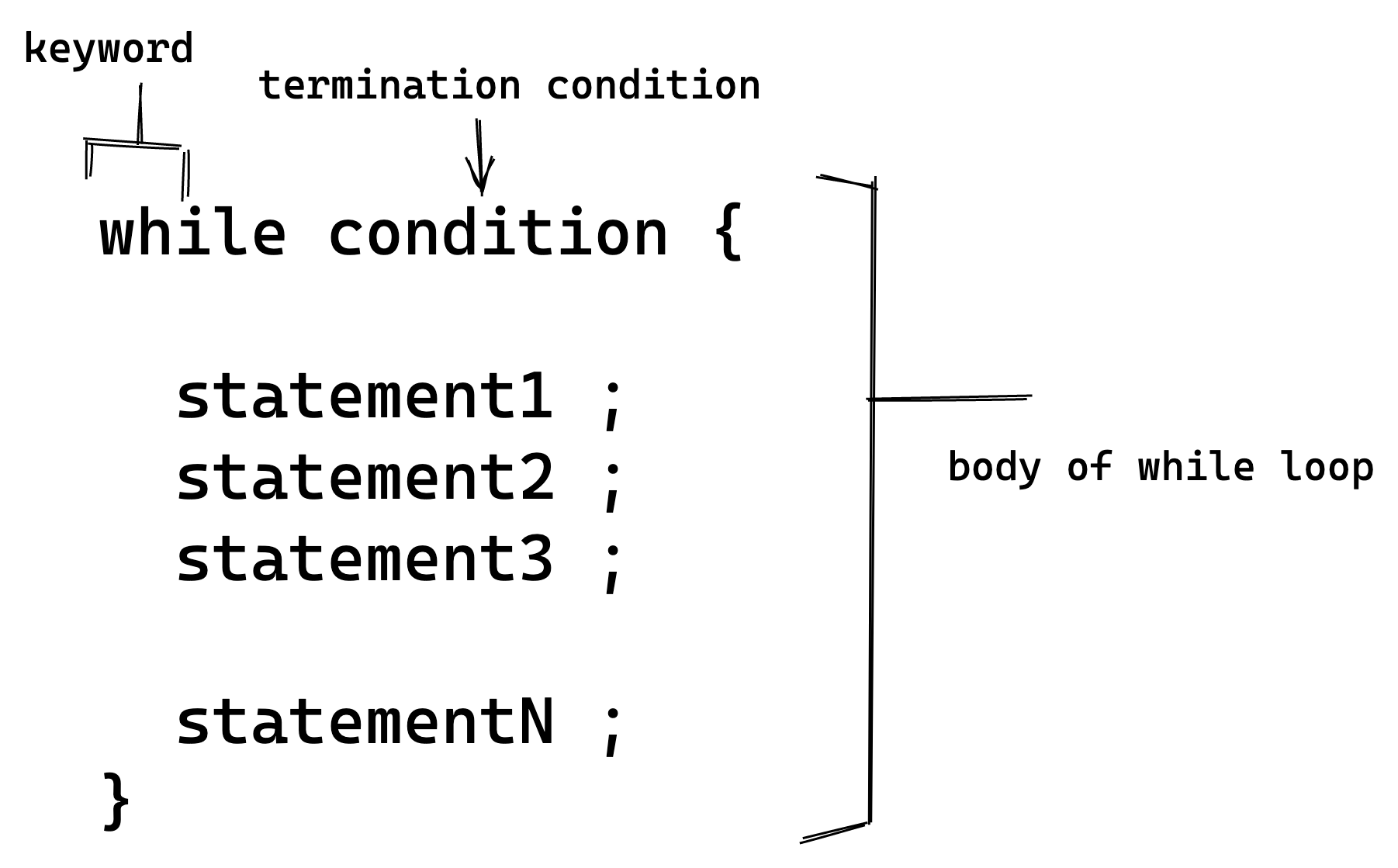
- Syntax The while keyword is followed by a condition that must be true for the loop to continue iterating and then begins the body of the loop. the general syntax is :
- Example
The following example makes use of a while loop to print a variable value. The loop terminates when the variable’s value modulus 3 equals 1
fn main() {
let mut var = 1; //define an integer variable
let mut found = false; // define a boolean variable
// define a while loop
while !found {
var=var+1;
//print the variable
println!("{}", var);
// if the modulus of variable is 1 then found is equal to true
if var % 3 == 1 {
found = true;
}
println!("Loop runs");
}
}
output
2
Loop runs
3
Loop runs
4
Loop runs
Explanation
- A mutable variable, var, is defined on line 2.
- A mutable variable, found, is defined on line 3.
while loop definition
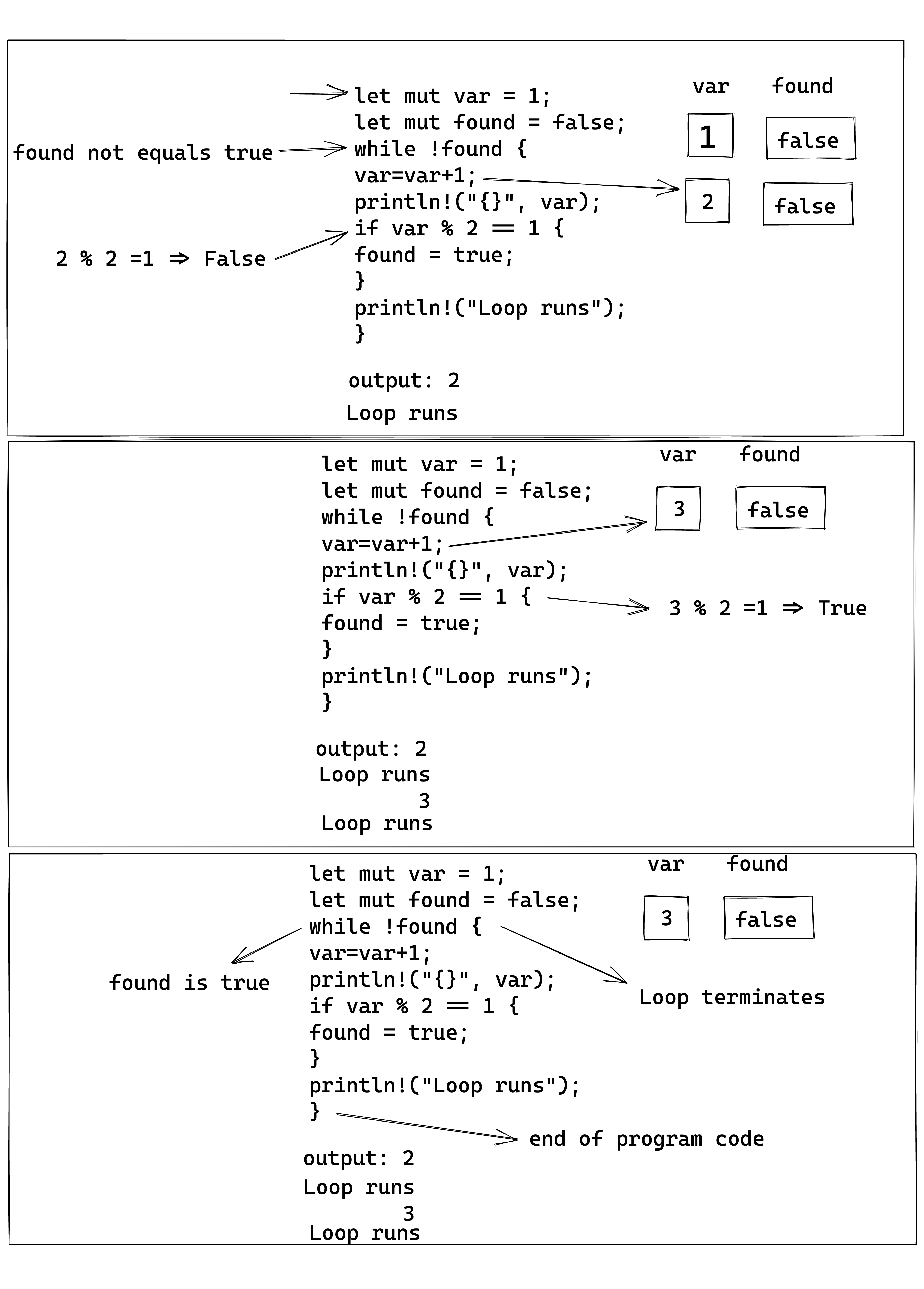
while loop is defined on line 5. while loop is followed by a variable found. found is initially set to false. !found means that the loop will continue to iterate until the value of found evaluates to be true.The loop terminates when found is set to true. From here the body of the while loop starts
while loop body
- The body of the loop is defined from line 5 to line 14.
- In each iteration:
- The value of the variable var is incremented by 1 on line 6 and then printed on line 8.
- If the value of the var modulus 3 is equal to 1, then the value of found is set to true else it prints “loop runs” on line 13 and the loop continues.
The following illustration traces the execution of the program:
Loop
If you want the iteration to continue infinitely, then use the loop keyword before the block of code.
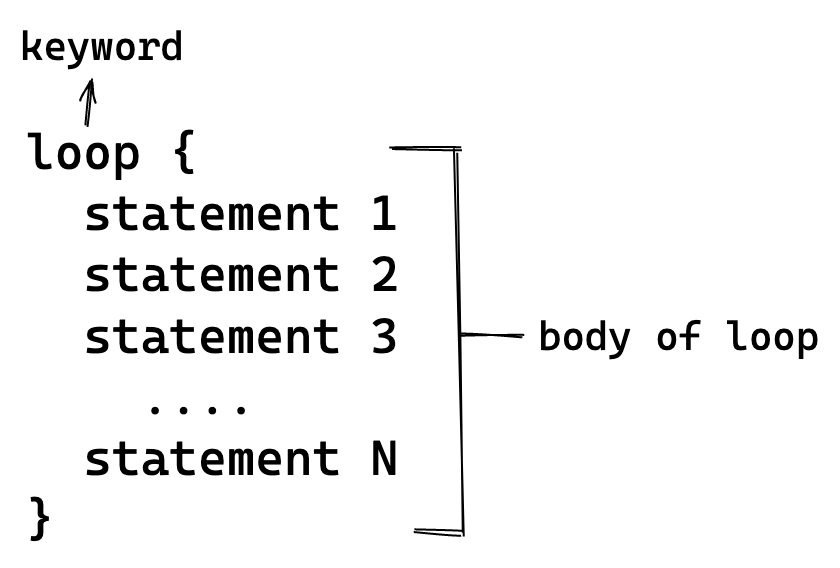
- Syntax
The loop keyword is followed by the body of the loop enclosed within curly brackets {}.
The general syntax is :
Example
The following example shows how the loop runs infinitely using a loop. Note: The maximum time that is set for the code to run on our platform is 30sec. Since the code below runs more than that, it won’t execute here. However, the code will continue to run indefinitely.
fn main() {
//define an integer variable
let mut var = 1;
// define a while loop
loop {
var = var + 1;
println!("{}", var);
}
}
output:
Loop continues infinite times
Explanation
A mutable variable var is defined on line 3.
loop definition
- loop is defined on line 5.
From here the body of the loop starts
- loop body
- The body of the loop is defined from line 5 to line 8.
- In each iteration, the value of the variable var is incremented by 1 on line 6 and then printed on line 7.
- The loop continues to iterate infinitely.
Quiz
Test your understanding of indefinite loops.
- [ ] for - [ ] while - [ ] loop # In a loop that has no terminating condition, which of the following is true?
- [ ] program will give an error - [ ] program will run indefinite times # How many times does the loop run? ``` fn main() { let mut var = 1; //define an integer variable let mut found = false; // define a boolean variable // define a while loop while !found { var=var+1; //print the variable println!("{}", var); // if the modulus of variable is 1 then found is equal to true if var % 3 == 1 { found = true; } println!("Loop runs"); } } ``` - [ ] 1 - [ ] 2 - [ ] 3
Last updated 25 Jan 2024, 05:11 +0530 .